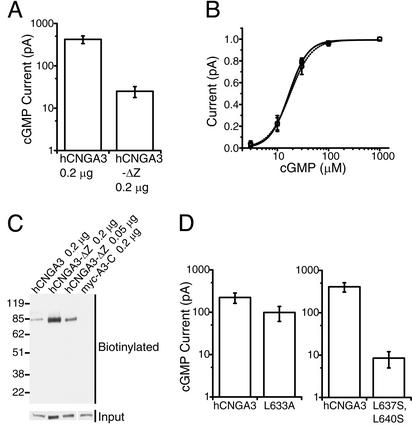
Figure 2.
Involvement of CLZ domain in assembly of functional CNG A homomeric channels. (A) Saturated cGMP-activated current amplitudes from excised patches containing expressed hCNGA3 or hCNGA3-ΔZ (hCNGA3 with L626–L647 deleted). Means (±SEM) are 421 ± 87 pA (Left, 14 patches) and 25 ± 7 pA (Right, 17 patches). (B) cGMP dose–response relations of expressed hCNGA3 (squares and solid line, eight patches) and hCNGA3-ΔZ (circles and dashed line, nine patches). Data were normalized to currents activated by 1 mM cGMP and fitted by the Hill equation with K1/2 = 16.9 μM, n = 2.3 (hCNGA3), and K1/2 = 17.8 μM, n = 2.1 (hCNGA3-ΔZ). The error bars are SDs. (C) Levels of biotinylated hCNGA3, hCNGA3-ΔZ, and presumably soluble myc-A3-C (myc-tagged cytoplasmic C terminus of hCNGA3, negative control) are compared. The surface proteins of transfected 293T cells were labeled with a membrane-impermeant biotinylation reagent. The biotinylated proteins were purified with avidin beads and subjected to immunoblot analysis with the antibody (JH 1857) against the C terminus of hCNGA3. (D) Saturated cGMP-activated current amplitudes from hCNGA3 vs. two mutant channels carrying point mutations in their CLZ domains (L633A and L637S, L640S). Means (±SEM) are 223 ± 61 pA (Left, 13 patches, hCNGA3), 98 ± 38 pA (Left, 14 patches, L633A), 410 ± 102 pA (Right, 15 patches, hCNGA3), and 8.5 ± 3.5 pA (Right, 15 patches, L637S, L640S).