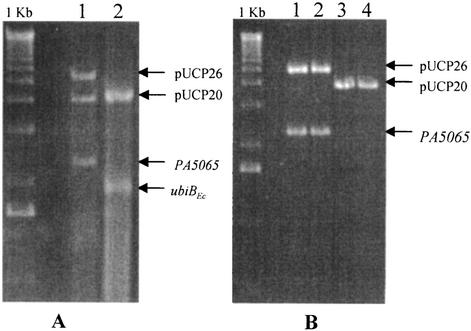
FIG. 2.
Analysis of plasmids isolated from recombinant PA5065::Gmr insertional mutants. (A) Plasmid DNA was isolated from the recombinant PA5065::Gmr/pUCP26-PA5065 strain after transformation with pUCP20 (lane 1) or pUCP20-ubiBEc (lane 2) and digested with EcoRI and HindIII to release the inserts. pUCP26-PA5065 was isolated in tandem with pUCP20 (lane 1) despite counterselection, but it was lost if pUCP20-ubiBEc was present in the cell (lane 2). (B) The plasmid DNA isolated from PA5065::Gmr/pUCP26-PA5065 was used to transform E. coli JM109, which was grown on plates containing either 15 μg of tetracycline/ml or 50 μg of ampicillin/ml. Analysis of plasmid DNA isolated from the resulting Tetr (lanes 1 and 2) and Ampr (lanes 3 and 4) recombinant E. coli strains by digestion with EcoRI and HindIII confirmed that both plasmids were originally present in the recombinant P. aeruginosa mutant despite counterselection against pUCP26-PA5065.