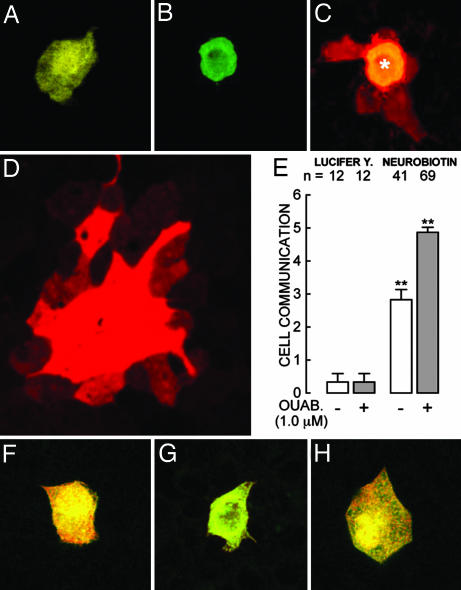
Fig. 2.
Gap junctions and their sensitivity to ouabain. (A–E) Cocultures of R and W cells. (A) Lucifer yellow can be observed directly under the same microscope used to impale the cells. (B) Neurobiotin does not fluoresce under this optics; therefore, to gauge the injection this probe was coinjected with fluorescent (FITC)-dextran of 20 kDa (green) that does not diffuse to neighboring cells. Monolayers were then fixed and stained with TRITC-conjugated streptavidin (red). (C) Confocal micrograph of a cell injected with dextran (∗) plus neurobiotin that diffuses to several nearest neighbors. (D) In ouabain-treated monolayers neurobiotin propagates to secondarily connected cells, and the area of stained cells becomes considerably larger. This picture was taken at one-half of the magnification of the other six to show the whole area of stained cells. (E) The first pair of bars corresponds to cells injected with Lucifer yellow, and the second pair of bars corresponds to cells injected with neurobiotin both in the absence (open bars) and presence (gray bars) of ouabain. Neurobiotin does not diffuse to neighboring cells in confluent monolayers of pure cell types. (F) An R cell (of 10) showing that the probe remains within the injected cell. (G) Another R cell (of 10) treated with ouabain for 24 h. (H) A W cell (of 10) cultured under control conditions. This test cannot be performed in W cells treated with ouabain because they detach and abandon the monolayer.