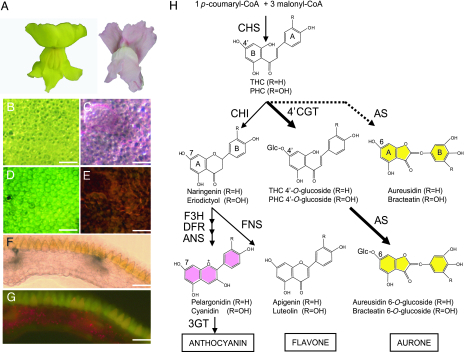
Fig. 1.
Flavonoids and their biosynthetic pathway in A. majus. (A) Flower colors in A. majus cultivar (cv.) Snap Yellow (Left) and cv. Merryland Pink (Right). Shown are petal color on the adaxial side of cv. Snap Yellow (B) and of cv. Merryland Pink (C). Fluorescent microcopies in cv. Snap Yellow (D) and Merryland Pink (E). Cross sections show that fluorescence is restricted to the pigmented adaxial epidermis of cv. Snap Yellow (F and G). (Scale bar: 100 μm.) (H) Flavonoid biosynthetic pathway. The 4′ position of chalcones corresponds to the 6 position of aurones and the 7 position of flavanone (naringenin). Dotted arrow, aurone biosynthetic activity of AmAS1 in vitro; thick arrows, the aurone biosynthetic pathway in vivo reported in this study; thin arrows, the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway; CHS, chalcone synthase; CHI, chalcone isomerase; F3H, flavanone 3-hydroxylase; DFR, dihydroflavonol 4-reductase; ANS, anthocyanindin synthase; 3GT, anthocyanin 3-O-glucosyltransferase; FNS, flavone synthase; AS, aureusidin synthase; 4′CGT, chalcone 4′-O-glucosyltransferase; THC, tetrahydroxychalcone; PHC, pentahydroxychalcone; Glc, glucose.