Fig. 3.
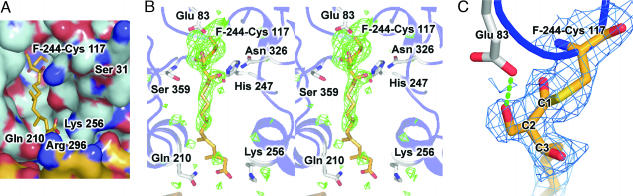
Overview of HMGS in complex with F-244. (A) Electrostatic surface of HMGS covalently bound to ring-opened F-244. Color-coding is identical to Fig. 2A. The inhibitor F-244 does not occupy the same part of the pantothenate-binding tunnel as the CoA tail shown in Fig. 2A. (B) Stereoview of the HMGS active site for the ring-opened F-244 covalent complex. Color-coding and map calculations are identical to Fig. 2B. The first eight carbons of the acyl tail of F-244 are well ordered; however, the position of the remaining six carbons display much weaker electron density as the tail protrudes out of the active site entrance. (C) Close-up view of the HMGS active site for the ring-opened F-244 covalent complex. The SIGMAA-weighted 2Fo − Fc electron density map is shown in blue, contoured at 1σ. A H-bond between Glu-83 and the 2-hydroxymethyl moiety of ring-opened F-244 is shown as rendered green cylinders.