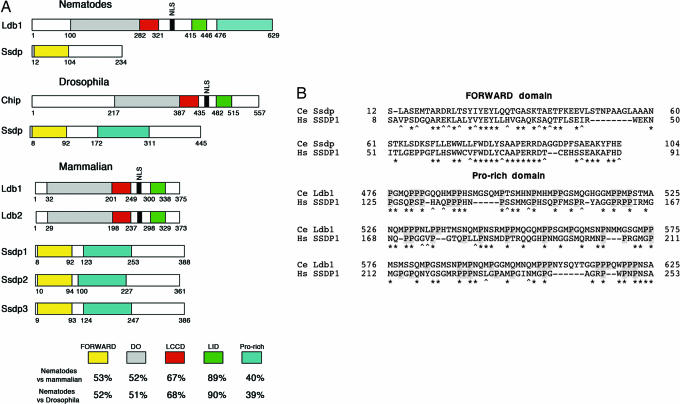
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic comparison of Ldb1 and Ssdp proteins. (A) Domain architecture of the invertebrate and vertebrate Ssdp and Ldb proteins. At the bottom, homology is shown as percent similarity between corresponding domains. DD, dimerization domain; LCCD, Ldb1-Chip conservative domain; LID, LIM-interaction domain; Pro-rich, proline-rich sequence. Amino acid numbers in diagrams of nematode and mammalian proteins are shown for C. elegans and human, respectively. (B) Alignment of the proline-rich regions of Ssdp1 and Ldb1. Ce, C. elegans; Hs, Homo sapiens. Prolines are on a gray background. Identical amino acids are indicated by asterisks, and conserved amino acid substitutions are indicated by carets. Spaces were introduced to optimize the alignment, and they are indicated by dashes. Amino acid numbers are shown to the left and to the right of the corresponding sequences.