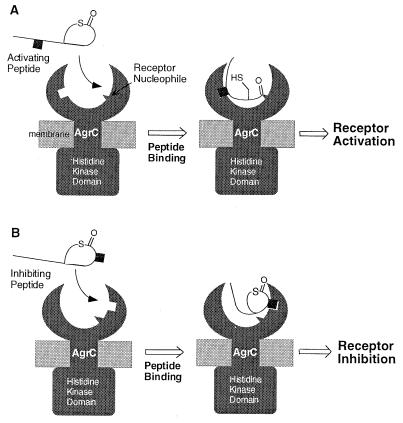
Figure 5.
Proposed model for the activation and the inhibition of the agr response. (A) Activation of the agr response occurs when an AgrD peptide interacts with an AgrC receptor from the same S. aureus class. Specific AgrD–AgrC interactions lead to the thiol ester group within the peptide being positioned close to a nucleophile within the receptor. Subsequent trans-acylation leads to a signal-transducing conformational change in the receptor, which may include homodimerization and trans-phosphorylation of the histidine kinase domains. (B) Inhibition of the agr response occurs via an interclass, noncovalent interaction that serves to exclude the strain’s own activating peptide from the receptor.