Figure 4. Loss of cpa causes excessive actin polymerization.
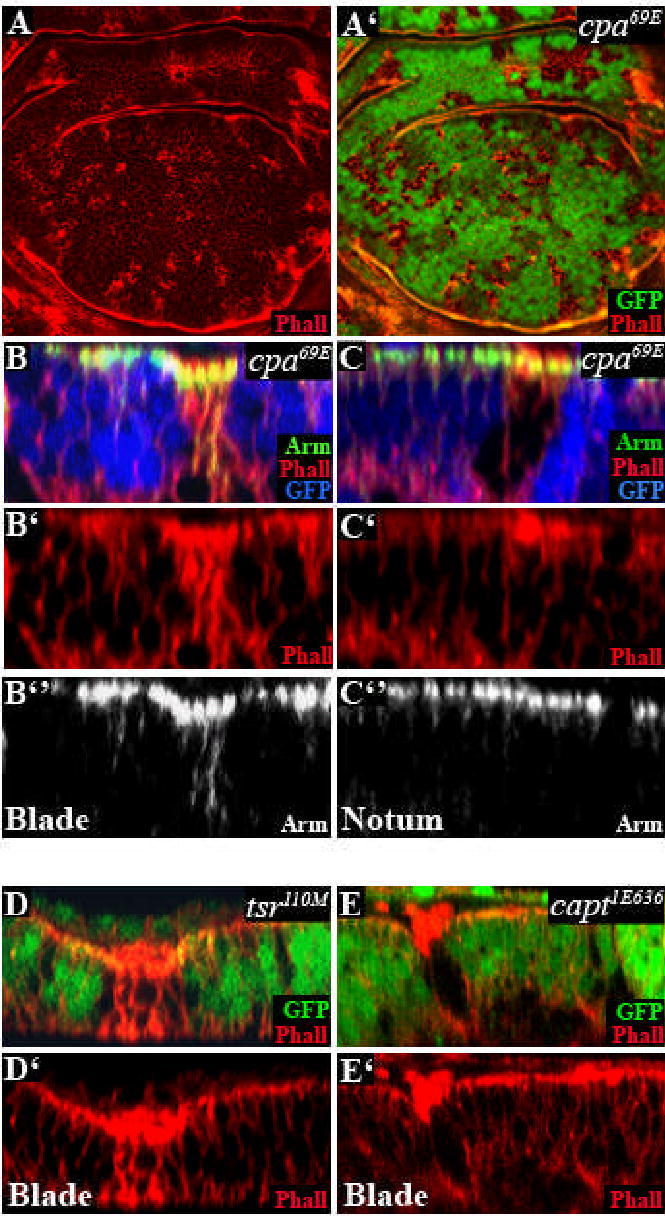
All panels show third instar wing discs in which clones are marked by the absence of GFP (green in A’,D,E or blue in B,C) and stained with TRITC-phalloidin to reveal F-actin (red in A,A’,B,B’,C,C’,D,D’,E,E’)) and anti-Arm (green in B,C or white in B”,C”). (A) standard confocal sections; (B–E) optical cross sections. (A–C) cpa69E mutant clones in the notum (C) or the blade (B) primordium. cpa mutant clones accumulate actin filaments near the apical cell membrane in the notum but throughout the cell in the blade primordium. (D) tsr110M or (E) captE636 mutant clones.
