Fig. 1. Characterization of the Ftz-F1-Containing YAC, ySLH1.
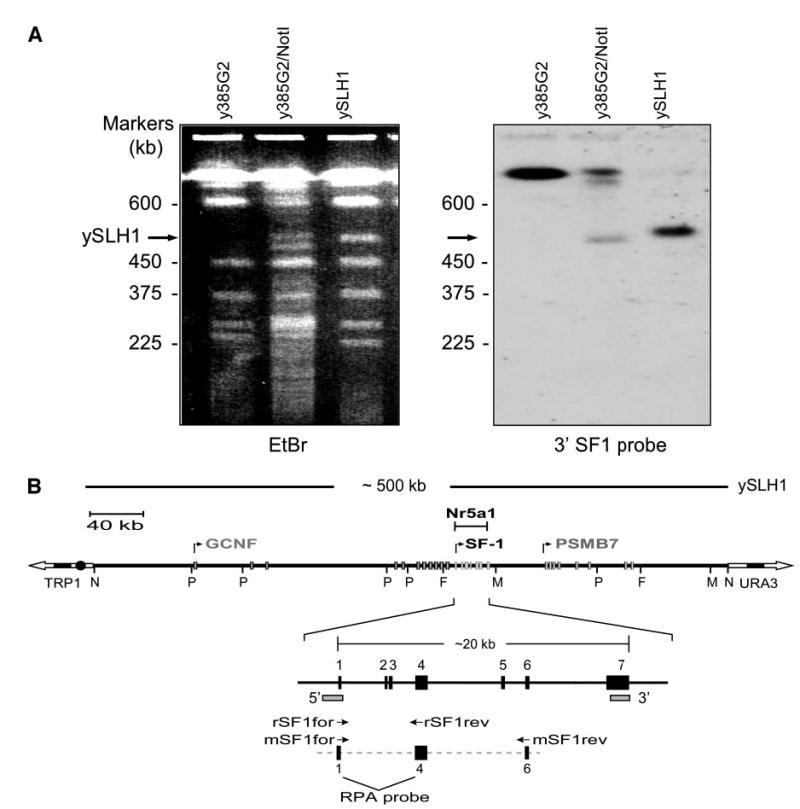
A, Pulse field electrophoresis of y385G2, y385G2 digested with NotI, and ySLH1, a 500-kb NotI subclone of y385G2. The gel was stained with ethidium bromide (EtBr, left) and characterized by Southern blot analysis (right) using the 3’SF1 probe (shown in B as 3′-marked rectangle). B, Schematic depiction of ySLH1. ySLH1-containing yeast were subject to digestion with restriction endonucleases and analyzed by PFGE and Southern blot analysis (not shown). Positions of the restriction endonuclease sites for PmeI (P), NotI (N), FseI (F), and MluI (M) were determined using 5′ and 3′ probes (marked as rectangles) and TRP1 and URA3 probes corresponding to the vector arms. Three different contigs (AC108347, AC119301, AC129763) from the working draft sequence of the rat genome project were assembled to generate a map of the rat Ftz-F1 locus and the positions of the above restriction endonuclease sites were confirmed. Annotated are the Ftz-F1 gene and its adjacent genes encoding a second orphan nuclear receptor GCNF (NR6A1) and a proteosome protein PSMB7. Boxes represent the different genes’ exons and arrows the direction and start of transcription. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of rat SF-1 (rSF1for and rSF1rev) and mouse SF-1 (mSF1for and mSF1rev) are indicated as are exons within the probe employed for RNAse protection analysis.
