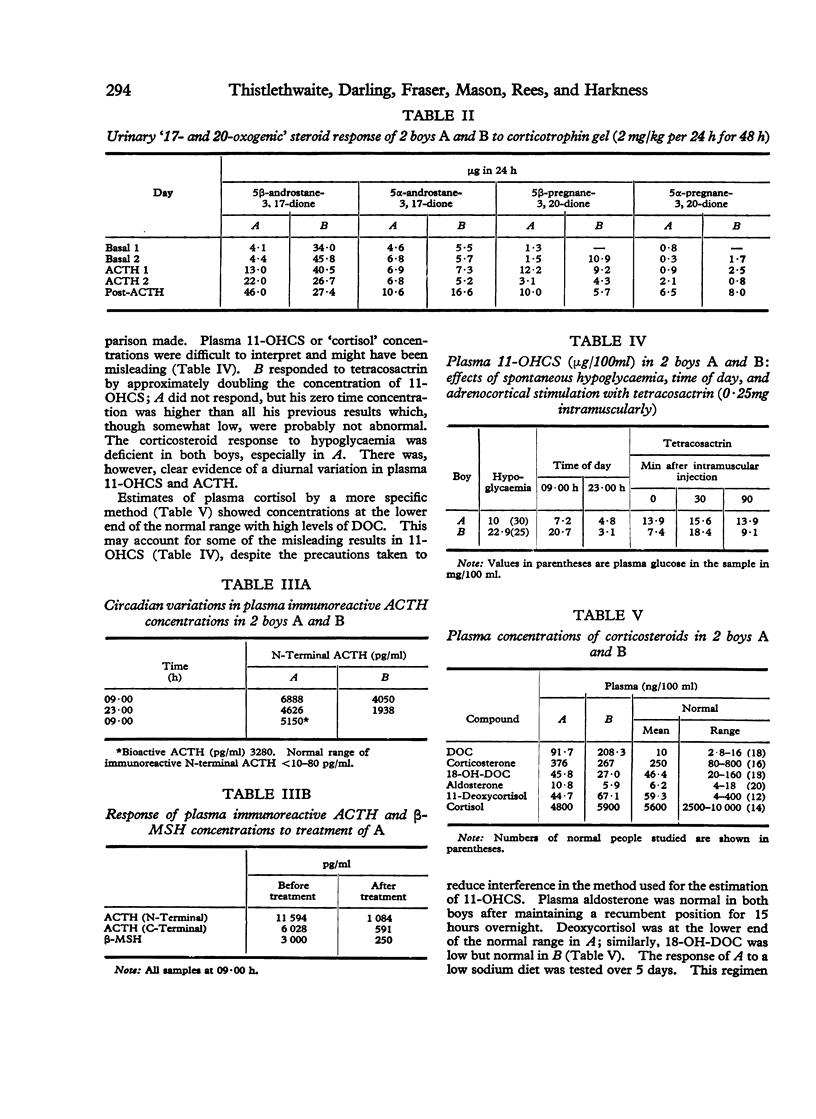
Abstract
The clinical and biochemical findings are described in 2 brothers who had intermittent hypoglycaemia generally precipitated by the "stress" of infection. Both were tall and pigmented. Both boys showed a failure of adrenocortical response to ACTH which was progressive in the eldest boy. The diagnosis of familial glucocorticoid deficiency (hereditary adrenocortical unresponsiveness) was confirmed by the absence of electrolyte imbalance even on a low sodium diet, and by very high levels of ACTH in plasma. High levels of deoxycorticosterone (DOC) were found in both children with normal levels of other plasma corticosteroids. It is suggested that the high levels of DOC may be in some way related to the apparent persistence of a "fetal" type of adrenocortical steroid biosynthesis for 18 months or more in these boys. After the diagnosis, established by relatively simple methods, treatment with cortisone acetate has 0een highly effective.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berson S. A., Yalow R. S. Radioimmunoassay of ACTH in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2725–2751. doi: 10.1172/JCI105955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besser G. M., Cullen D. R., Irvine W. J., Ratcliffe J. G., Landon J. Immunoreactive corticotrophin levels in adrenocortical insufficiency. Br Med J. 1971 Feb 13;1(5745):374–376. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5745.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besser G. M., Orth D. N., Nicholson W. E., Byyny R. L., Abe K., Woodham J. P. Dissociation of the disappearance of bioactive and radioimmunoreactive ACTH from plasma in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 May;32(5):595–603. doi: 10.1210/jcem-32-5-595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. D., Strott C. A. Plasma deoxycorticosterone in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Jun;32(6):744–750. doi: 10.1210/jcem-32-6-744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAYTON B. E., EDWARDS R. W., RENWICK A. G. Adrenal function in children. Arch Dis Child. 1963 Feb;38:49–53. doi: 10.1136/adc.38.197.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling J. A., Harkness R. A. A method for the group analysis of steroids in milk. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1973 Feb;72(2):391–400. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0720391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling J. A., Kelly R. W., Laing A. H., Harkness R. A. The isolation and identification of progesterone obtained from cows' milk during pregnancy. J Endocrinol. 1972 Aug;54(2):347–348. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0540347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald R. A., Toth A. A comparison of the -melanocyte-stimulating hormone and corticotropin response to hypoglycemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 May;36(5):925–930. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-5-925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exley D., Chamberlain J. Properties of steroidal 3 enol heptafluorobutyrates. Steroids. 1967 Nov;10(5):509–526. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(67)90126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEW J. D. A method for the analysis of urinary 17-hydroxycorticosteroids. J Endocrinol. 1961 Mar;22:31–46. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0220031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fevold H. R., Drummond H. B. Factors affecting the adrenocorticotropic hormone stimulation of rabbit adrenal 17alpha-hydroxylase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 20;313(1):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90202-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser I. S., Baird D. T., Hobson B. M., Michie E. A., Hunter W. Cyclical ovarian function in women with congenital absence of the uterus and vagina. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Apr;36(4):634–637. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-4-634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. N. Mechanism of ACTH action. Metabolism. 1972 Jun;21(6):571–588. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(72)90101-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson J. A., Gustafsson S., Olin P. Steroid excretion patterns in urine from two boys in the neonatal period with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1972 Oct;71(2):353–364. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0710353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkness R. A., Love D. N. Studies on the estimation of urinary pregnanetriol during pregnancy and childhood. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1966 Apr;51(4):526–534. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0510526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe A. The mammalian pars intermedia: a review of its structure and function. J Endocrinol. 1973 Nov;59(2):385–409. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0590385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter W. M., Greenwood F. C. A radio-immunoelectrophoretic assay for human growth hormone. Biochem J. 1964 Apr;91(1):43–56. doi: 10.1042/bj0910043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine W. J., Toft A. D., Hunter W. M., Kirkham K. E. An assessment of plasma TSH radioimmunoassay and of the TSH stimulation test in the diagnosis of 100 consecutive patients with suspected hypothyroidism. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1973 Apr;2(2):135–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1973.tb00413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelch R. P., Kaplan S. L., Biglieri E. G., Daniels G. H., Epstein C. J., Grumbach M. M. Hereditary adrenocortical unresponsiveness to adrenocorticotropic hormone. J Pediatr. 1972 Oct;81(4):726–736. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kershnar A. K., Roe T. F., Kogut M. D. Adrenocorticotropic hormone unresponsiveness: report of a girl with excessive growth and review of 16 reported cases. J Pediatr. 1972 Apr;80(4):610–619. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80058-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. P., Baden M., Giroud C. J. Quantitative measurement and significance of 5 plasma corticosteroids during the perinatal period. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 May;36(5):944–950. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-5-944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPSCOMB H. S., NELSON D. H. A sensitive biologic assay for ACTH. Endocrinology. 1962 Jul;71:13–23. doi: 10.1210/endo-71-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTINGLY D. A simple fluorimetric method for the estimation of free 11-hydroxycorticoids in human plasma. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Jul;15:374–379. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.4.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason P. A., Fraser R. Estimation of aldosterone, 11-deoxycorticosterone, 18-hydroxy-11-deoxy-corticosterone, corticosterone, cortisol and 11-deoxycortisol in human plasma by gas-liquid chromatography with electron capture detection. J Endocrinol. 1975 Feb;64(2):277–288. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0640277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon C. J., Kenny E. M., Kowarski A., Snipes C. A., Spaulding J. S., Finkelstein J. W., Blizzard R. M. The syndrome of congenital adrenocortical unresponsiveness to ACTH. Report of six cases. Pediatr Res. 1968 Nov;2(6):501–513. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196811000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moshang T., Jr, Rosenfield R. L., Bongiovanni A. M., Parks J. S., Amrhein J. A. Familial glucocorticoid insufficiency. J Pediatr. 1973 May;82(5):821–826. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEY R. L., SHIMIZU N., NICHOLSON W. E., ISLAND D. P., LIDDLE G. W. CORRELATION OF PLASMA ACTH CONCENTRATION WITH ADRENOCORTICAL RESPONSE IN NORMAL HUMAN SUBJECTS, SURGICAL PATIENTS, AND PATIENTS WITH CUSHING'S DISEASE. J Clin Invest. 1963 Nov;42:1669–1677. doi: 10.1172/JCI104853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees L. H., Cook D. M., Kendall J. W., Allen C. F., Kramer R. M., Ratcliffe J. G., Knight R. A. A radioimmunoassay for rat plasma ACTH. Endocrinology. 1971 Jul;89(1):254–261. doi: 10.1210/endo-89-1-254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root A. W., Bongiovanni A. M., Eberlein W. R. Studies of the secretion and metabolic effects of human growth hormone in children with glucocorticoid-induced growth retardation. J Pediatr. 1969 Nov;75(5):826–832. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPARD T. H., LANDING B. H., MASON D. G. Familial Addison's disease; case reports of two sisters with corticoid deficiency unassociated with hypoaldosteronism. AMA J Dis Child. 1959 Feb;97(2):154–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOYKA L. F., CRAWFORD J. D. ANTAGONISM BY CORTISONE OF THE LINEAR GROWTH INDUCED IN HYPOPITUITARY PATIENTS AND HYPOPHYSECTOMIZED RATS BY HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Apr;25:469–475. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-4-469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schambelan M., Biglieri E. G. Deoxycorticosterone production and regulation in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Apr;34(4):695–703. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-4-695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackleton C. H., Mitchell F. L., Farquhar J. W. Difficulties in the diagnosis of the adrenogenital syndrome in infancy. Pediatrics. 1972 Feb;49(2):198–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Budd M. A., Efron M. L., Isselbacher K. J. Isovaleric acidemia: a new genetic defect of leucine metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):236–242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez A. M., Schutt-Aine J. C., Kenny F. M. Effect of cortisone therapy on the diurnal pattern of growth hormone secretion in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Pediatr. 1972 Mar;80(3):433–440. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80501-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A., Fraser R. The estimation of plasma 11-deoxycorticosterone in man using gas-liquid chromatography with electron capture detection. J Endocrinol. 1971 Nov;51(3):557–567. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0510557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


