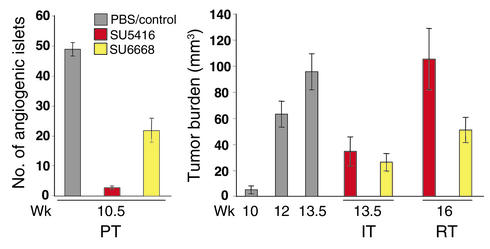
Figure 1.
Different stage-specific efficacy profiles for the VEGFR inhibitor SU5416 and the PDGF (+VEGF/FGF) receptor inhibitor SU6668 in the three distinct stages of pancreatic islet carcinogenesis in RIP1Tag2 transgenic mice. Mice were either treated with SU5416 or SU6668 as described in Methods. The average number of angiogenic islets ± SEM at 10.5 weeks in control and treated mice, the average tumor burden ± SEM in PBS/vehicle–treated mice (at 10, 12, 13.5 weeks), and SU5416- and SU6668-treated mice (at 13.5 and 16 weeks) are shown. The prevention trial (PT) started at 5 weeks, when mice harbor hyperplastic/dysplastic islets, and ended at 10.5 weeks, when the first small tumors appear. Islets that have switched on angiogenesis are scored by their reddish color (resulting from microhemorrhage and leakiness associated with VEGF-induced angiogenesis). In the intervention trial (IT), mice with a small tumor burden (10 weeks) are treated until the end stage (13.5 weeks), while in the regression trial (RT), 12-week-old mice with substantial tumor burden and a life expectancy of less than 2 weeks are treated until 16 weeks, when control mice are already dead. Statistical analysis was performed with a two-tailed, unpaired Mann-Whitney test comparing experimental groups to PBS-injected control mice. Tumor burdens of experimental groups in the Regression Trial were compared to that of 12-week-old Rip1Tag2 mice. Cohorts of 6–21 animals were used. P values less than 0.1 are considered statistically significant. P values of SU5416 PT = 2.26 × 10–5, SU6668 PT = 0.0002, SU5416 IT = 0.0009, SU6668 IT = 0.0001, SU5416 RT = 0.1827, and SU6668 RT = 0.3228.