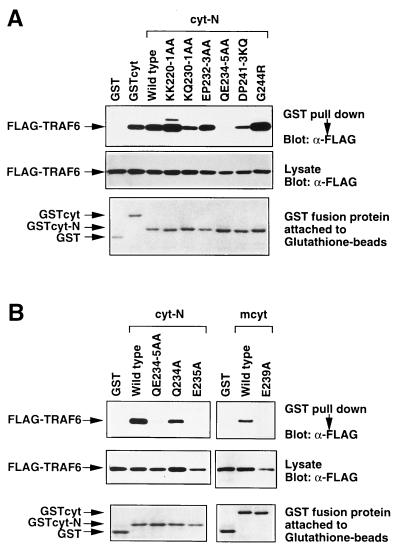
Figure 2.
Glu-235 in hCD40 is critical for TRAF6 binding. (A) TRAF6 binding with cyt-N was abolished by the QE234–5AA mutation. Conserved residues in the N-terminal poorly conserved region in hCD40cyt were mutated in the cyt-N deletion mutant, and each construct was tagged with GST. GST-tagged CD40 cytoplasmic domain or its mutants and Flag-tagged TRAF6 were transiently expressed in 293T cells and in vivo binding assays were performed. Association between Flag-TRAF6 and GST-tagged CD40 mutants (Top) and expression level of Flag-TRAF6 (Middle) and that of GST-tagged CD40 mutants (Bottom) are shown. (B) Single point mutation E235A abolished TRAF6 association with GST-CD40. (Left) Either Gln-234 or Glu-235 alone was mutated to Ala in the GST-tagged cyt-N deletion mutant. GST-tagged CD40cyt or its mutants and Flag-tagged TRAF6 were transiently coexpressed in 293T cells and in vivo binding assays were performed. Association between Flag-TRAF6 and GST-tagged CD40 mutants (Top) and expression level of Flag-tagged TRAF6 (Middle) and that of GST-tagged CD40 mutants (Bottom) are shown. (Right) Glu-239 in mCD40, corresponding to Glu-235 in hCD40, was mutated to Ala in GST-tagged full-length cyt of mCD40. In vivo binding assay between mCD40 and TRAF6 in 293T cells was performed as described above.