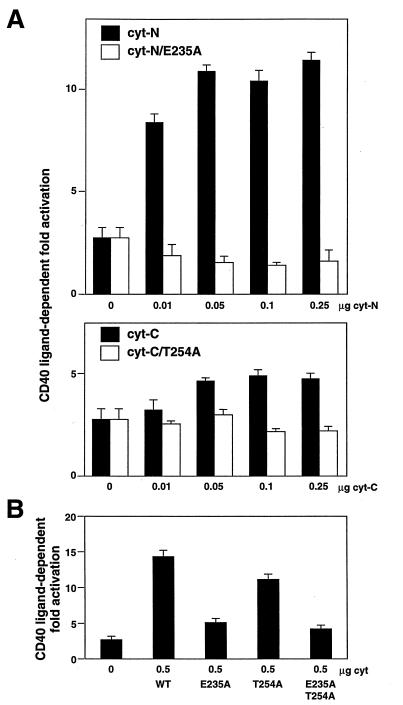
Figure 4.
Effects of E235A and T254A mutations on the CD40-mediated NFκB activation. (A) NFκB activation by CD40cyt-N was completely abolished by the E235A mutation. (Upper) CD40L-dependent fold activation of NFκB by CD40cyt-N (closed bar) and that by CD40cyt-N E235A (open bar) are shown. (Lower) CD40L-dependent fold activation of NFκB by CD40cyt-C (closed bar) and that by CD40cyt-C T254A (open bar) are shown. (B) Effects of E235A and T254A mutations on NFκB activation by the full-length CD40. CD40L-dependent fold activation of NFκB by the full-length CD40 with various mutatons is shown. Jurkat cells (2 × 106) were transfected with 0.5 μg of 3xκB-Luc, 0.5 μg of β-actin-β-gal, the indicated amounts of pME-hCD40 construct, 0 μg or 0.5 μg of pME-hCD40L, and enough pME18S control plasmid to give 5 μg of total DNA by the DEAE-dextran method. Cell extracts prepared at 36 hr after transfection were used for the luciferase assay. Fold activation was expressed as the ratio of luciferase activity with CD40L expression to that without CD40L expression. Values correspond to means ± SEMs of at least three independent experiments.