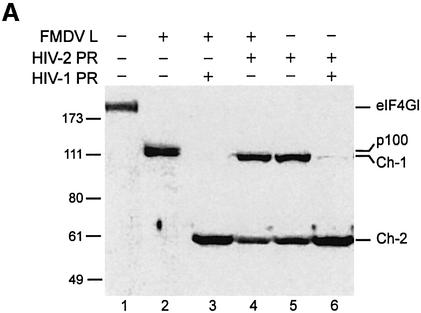
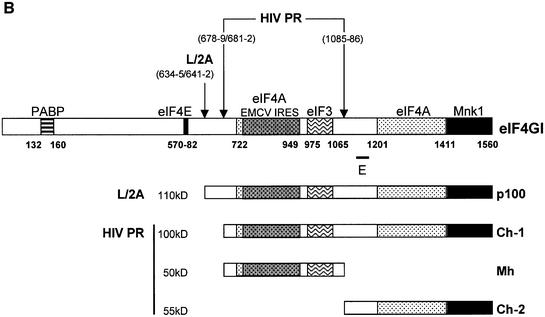
Fig. 2. Characterization of the C-terminal cleavage sites of eIF4GI. (A) RRL (10 µl) was incubated without (lane 1) or with L protease (1 µl, lanes 2–4) or HIV-2 PR (10 ng/µl, lanes 5 and 6), for 1 h at 30°C in a final volume of 20 µl. HIV-2 PR (20 ng/µl; lane 4) or 10 ng/µl HIV-1 PR (lanes 3 and 6) were then added and the mixture further incubated for 1 h. The samples were analysed by SDS–PAGE and western blotting as described in Figure 1. (B) The eIF4GI molecule is schematically represented with its different interaction domains for PABP and eIF4E (Gingras et al., 1999b), eIF4A (Lomakin et al., 2000; Morino et al., 2000), eIF3 (Korneeva et al., 2000), Mnk-1 (Morino et al., 2000) and the EMCV IRES (Lomakin et al., 2000). Cleavage sites for L/2A and HIV proteases, the obtained C-terminal fragments and the E epitope used for the western blot analysis are represented.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.