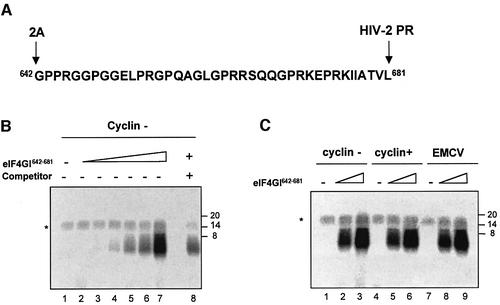
Fig. 7. eIF4GI642–681 can be crosslinked to various mRNAs. (A) Sequence of the 40 aa peptide (eIF4GI642–681), the 2A and HIV-2 cleavage sites are indicated on the figure. (B) Increasing amounts of chemically synthesized eIF4GI642–681 (lane 1, 0 µg; lane 2, 0.015 µg; lane 3, 0.030 µg; lane 4, 0.06 µg; lane 5, 0.12 µg; lane 6, 0.24 µg; lanes 7 and 8, 0.48 µg) was used in crosslinking assays with 32P-labelled uncapped cyclin probe (0.2 pmol; 75 000 c.p.m.) in the absence (lanes 1–7) or presence of unlabelled luciferase competitor (lane 8, 7 pmol). Following RNase A treatment, proteins were separated on 20% SDS–PAGE and the dried gel was exposed to autoradiography. The asterisk denotes a non-specific band which probably results from incomplete digestion of the radiolabelled transcript. (C) Crosslinking assays were performed in the absence (lanes 1, 4 and 7) or presence of chemically synthesized eIF4GI642–681 (lanes 2, 5 and 8, 0.25 µg; lanes 3, 6 and 9, 0.75 µg) with various 32P-labelled probes (75 000 c.p.m.): uncapped cyclin (lanes 1–3), capped cyclin (lanes 4–6) and uncapped EMCV (lanes 7–9). Following RNase A treatment, proteins were separated on 20% SDS–PAGE and the dried gel was subjected to autoradiography. Position of molecular weight markers are indicated on the right-hand side of the figure in kDa.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.