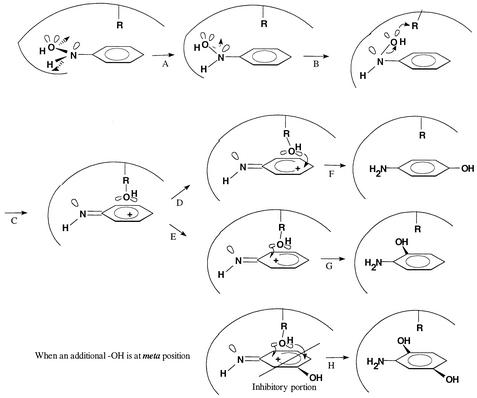
FIG. 6.
Hypothetical model for hydroxyl transfer mechanism during conversion of HAB catalyzed by the mutase from strain JMP134. (A) Mutase turns the O-N-C group away from the plane of the benzene ring to a position perpendicular to the ring; (B) the −OH group approaches an amino acid residue (R) of the enzyme; (C) an R-OH intermediate forms above the benzene ring; (D and F) the −OH moves to the para position to form 4-AP; (E and G) the −OH moves to the ortho position to form 2-AP; (H) the stereochemical effect of a hydroxyl group at the meta position inhibits the R-OH group accessible to the para position, resulting in the formation of the ortho isomer only.