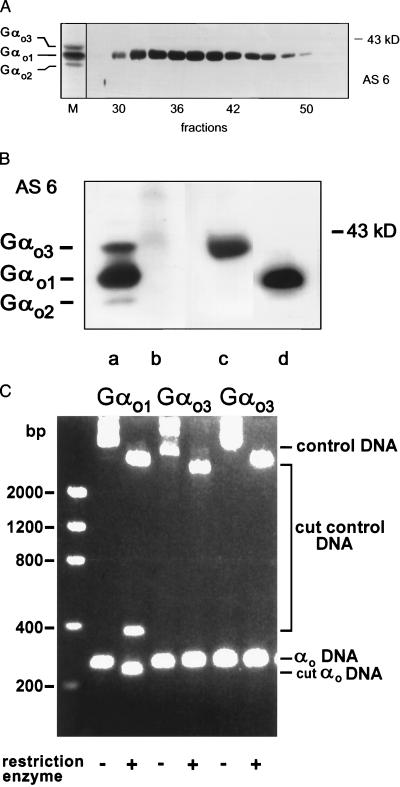
Figure 4.
(A) Immunoblot of fractions containing Gαo1 but not Gαo3 collected after rechromatography of purified Gαo1 using antiserum AS 6. The migration pattern of a purified mixture of three Gαo isoforms is shown on the left (M). (B) AS 6-stained immunoblot showing the mobilities of native murine brain Gαo isoforms (lane a) in comparison to recombinant murine Gαo1 (lane d) and Gαo3 (lane c). Lane b shows the absence of proteins after wild-type baculovirus infection of Sf9 cells. Apparent molecular mass of a marker protein is indicated. (C) Cleavage of Gαo-specific PCR products and control DNA by restriction enzymes. Total mRNA from rat brains was amplified by reverse transcription–PCR. While the forward primer was identical in all three experiments, reverse primers differed to generate additional restriction cleavage sites for AclI in the case of Gαo1, or AatII and EcoRV for the two possible Gαo3-specific sequences. The presence of cleavage sites generated by primer extension in PCR cycles was verified by a restriction digest with the appropriate enzymes. The amplified cDNAs and resulting cleavage products were separated on agarose gels and visualized by ethidium bromide staining. In the case of Gαo1 the intact PCR product (−; αo DNA) was 260 bp in length, whereas the cleaved product (+; cut αo DNA) had a length of 233 bp. The internal controls (control DNA) added were pcDNA3 for PCR products obtained with primers 1 and 3 and pQE60 in the experiment using primer 2. Note that cleavage of pcDNA3 by AclI resulted in an additional product of 373 bp (third lane from left). Positions of DNA standards are shown on the left.