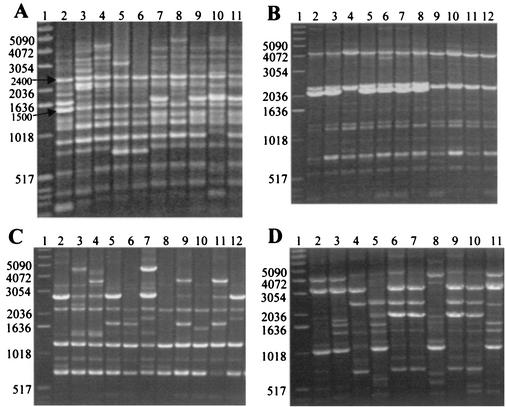
FIG. 1.
rep-PCR DNA fingerprints generated from Lactobacillus ATCC strains and vaginal isolates. The vaginal isolates were previously identified to the species level by using whole-chromosome probes produced from Lactobacillus ATCC strains. Each gel is representative of isolates having DNA homology to one Lactobacillus species. Clinical isolates within a group of Lactobacillus species were from different women. L. crispatus, L. jensenii, Lactobacillus sp. strain 1086V, and L. gasseri were chosen because of their vaginal prevalence. Lane 1 of each gel contains the 1-kb DNA size ladder. (A) Isolates homologous to the whole-chromosome probe of L. crispatus ATCC 33197. L. crispatus CTV-05 and ATCC 33197 are shown in lanes 2 and 3, respectively. Lanes 4 to 11 show the rep-PCR patterns for L. crispatus isolates from eight women. (B) Isolates homologous to the whole-chromosome probe of L. jensenii ATCC 25258. ATCC 25258 was run in lane 2. Lanes 3 to 12 show the rep-PCR patterns for 10 L. jensenii isolates, all from different women. (C) Isolates homologous to the Lactobacillus sp. strain 1086V whole-chromosome probe. The original Lactobacillus sp. strain 1086V is shown in lane 2. Lanes 3 to 12 show the rep-PCR patterns for Lactobacillus sp. strain 1086V-like isolates from nine women. (D) Isolates homologous to the whole-chromosome probe of L. gasseri ATCC 4963. L. gasseri ATCC 4963 and 9857 are shown in lanes 2 and 3, respectively. The rep-PCR DNA patterns for L. gasseri isolates from eight women are shown in lanes 4 to 11.