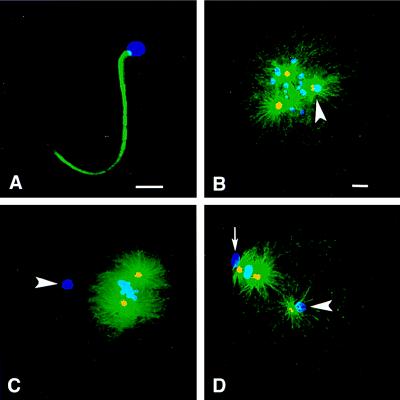
Figure 1.
Maternal vs. paternal aster formation in Spisula embryos. Shown is immunofluorescence of Spisula sperm (A) and embryos (B–D) during meiosis I and II by using anti-γ-tubulin antibody (yellow), antitubulin antibody (green), and ethidium homodimer to label chromatin (blue). (A) No γ-tubulin was detected in sperm before fertilization. (B) During prometaphase I, 10 min after fertilization, embryos contained two maternal asters and one sperm aster, and the paternal centrosome contained γ-tubulin and nucleated Mts (arrowhead). (C) During metaphase I, 20 min after fertilization, embryos contained two maternal asters but no sperm aster, and paternal centrosomes contained no γ-tubulin (arrowhead). (D) At metaphase of meiosis II, 40 min after fertilization, embryos again contained three asters, and the paternal centrosomes contained γ-tubulin and nucleated Mts (arrowhead). The small arrow in D indicates the first polar body. [Bars = 5 μm (A), and = 5 μm (B, for B–D).]