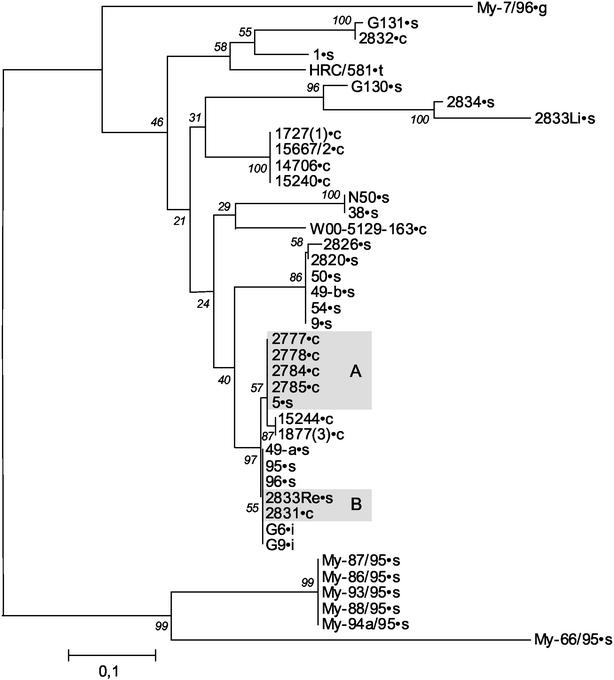
FIG. 2.
Representation of the phylogenetic relationship of the variable domain of lppS of all M. conjunctivae isolates analyzed. A distance matrix was calculated by the Jukes-Cantor algorithm (17), and a tree was built by the neighbor-joining method (22). Bootstrap values of 500 simulations are given at the branching points of the tree. The scale bar indicates the genetic distance of the variable segment of lppS as a ratio of different nucleotides. For clarity, we have labeled the different isolates with their origin by a point followed by a letter: c (chamois), g (goat), i (ibex), s (sheep), or t (type strain). The shaded boxes indicate isolates of the same strain found in sheep and neighboring chamois. “A” indicates the samples from animals from the Salzach valley, Austria, and “B” highlights the samples from animals from the San Bernardino region, Grisons, Switzerland.