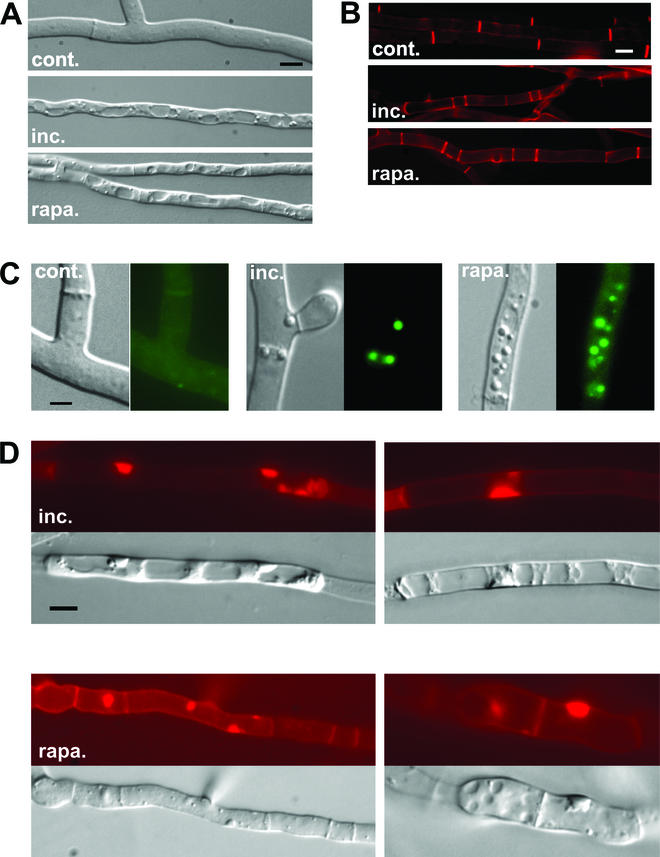
FIG.4.
het-R het-V incompatibility and rapamycin induce the same cytological alterations. (A, B, and C) The normal growth control (cont.), the het-R het-V incompatible strain (inc.), and the strains treated with rapamycin (at 200 ng · ml−1) (rapa.) are shown. (A) The intense vacuolization observed both during incompatibility and rapamycin treatment is shown. (B) Septa are labeled with Congo red. Note that septation is increased during incompatibility and rapamycin treatment. (C) Lipid body formation during incompatibility and rapamycin (200 ng · ml−1) treatment is shown. For each panel, the Nomarski view is given on the left and the fluorescence of the Nile red lipophilic dye is given on the right. (D) Abnormal deposition of cell wall induced by het-R het-V incompatibility and rapamycin (at 500 ng · ml−1) is shown. The two upper panels correspond to het-R het-V incompatibility. The lower panels correspond to rapamycin treatment. In each case the Nomarski view and the Congo red fluorescence specific of cell wall material are given. The scale bar represents 2 μm.