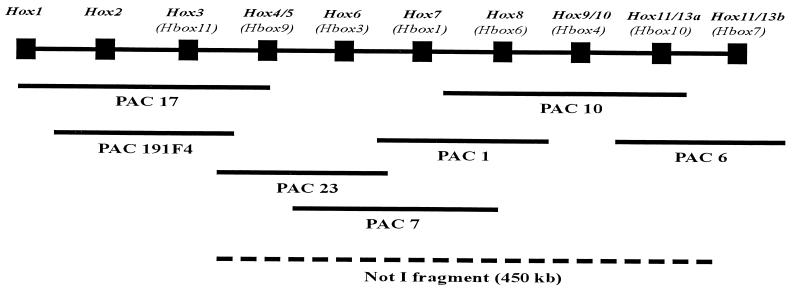
Figure 4.
Organization of the S. purpuratus Hox gene cluster. The diagram is not to scale, as the intergenic distances within the cluster have not been determined. The sequence of Hox genes within the cluster was inferred from their locations within PAC and BAC genomic inserts (see text) and the overlaps amongst clones containing each gene. For brevity, only one set of PAC genomic clones is shown, though each genomic region was analyzed on the basis of overlaps of multiple independent PAC and BAC clones. The correct names of the Hox genes with respect to their paralogous affinities with vertebrate Hox genes appear at the top of the diagram, and beneath in parentheses are designations found in earlier literature describing isolations of Hox homeodomains or cDNAs in various laboratories (see text for references). The dashed line indicates the span of the 450-kb fragment indicated in Fig. 3, which includes all the genes from SpHox4/5 to SpHox11/13a.