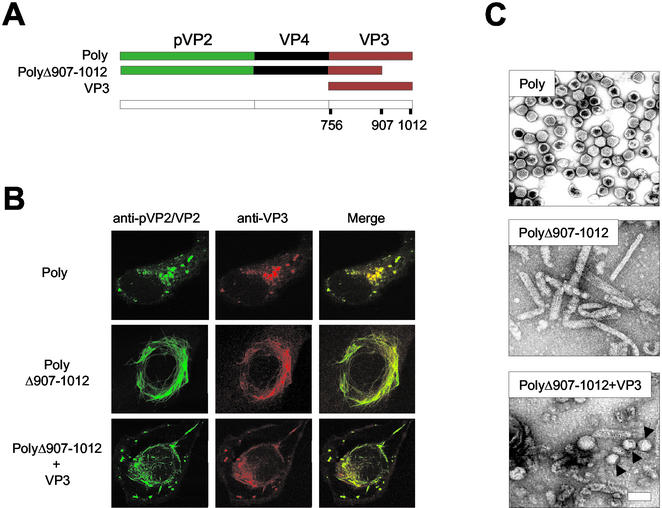
FIG. 1.
Effect of VP3 C-terminal deletion on VLP morphogenesis. (A) The diagram depicts the IBDV-derived genes expressed by the different rVVs used to test the effect of the VP3 C-terminal deletion on VLP formation in mammalian cells. VT7/Poly expresses the wild-type polyprotein. VT7/PolyΔ907-1012 expresses a deleted form of the polyprotein lacking the 105 C-terminal residues. VT7/VP3 expresses full-length VP3. (B) Effect of VP3 C-terminal deletion on pVP2/VP2 subcellular distribution. Digital confocal images of cells infected with VT7/Poly pr VT7/PolyΔ907-1012 or coinfected with VT7/PolyΔ907-1012 and VT7/VP3. At 24 h postinfection, cells were fixed and incubated with rabbit anti-pVP2/VP2 and rat anti-VP3, followed by incubation with goat anti-rabbit immunoglobulin coupled to Alexa 488 (green) and goat anti-rat immunoglobulin coupled to Alexa 594 (red). (C) Effect of VP3 C-terminal deletion on VLP assembly. Extracts from cells infected with VT7/Poly or VT7/PolyΔ907-1012 or coinfected with VT7/PolyΔ907-1012 and VT7/VP3 were subjected to sucrose gradient fractionation. Fractions were spotted onto a carbon-filmed grid, negatively stained, and visualized by electron microscopy. The images represent assemblies detected in equivalent fractions from the three samples.