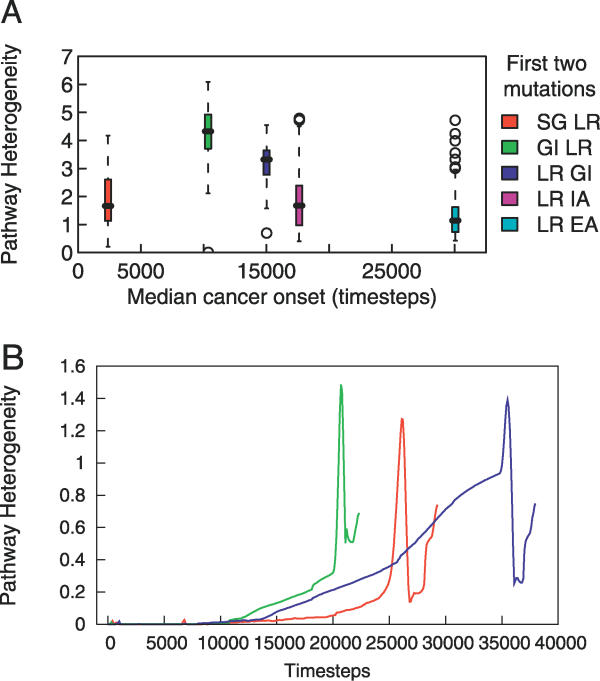
Figure 3. Tumor Heterogeneity.
(A) The five most common tumor categories, defined by the most common first two mutations, vary in their pathway heterogeneity.
(B) Example dynamics of heterogeneity during the development of three tumors. Each line corresponds to the development of one tumor; the red curve corresponds to the tumor discussed in the Sample Simulation Run section. As the tumor begins to form, there is typically a slow increase in the degree of tissue heterogeneity followed by a sudden increase, an equally sudden decrease, and then often another increase as the tissue reaches 9 × 105 cells.