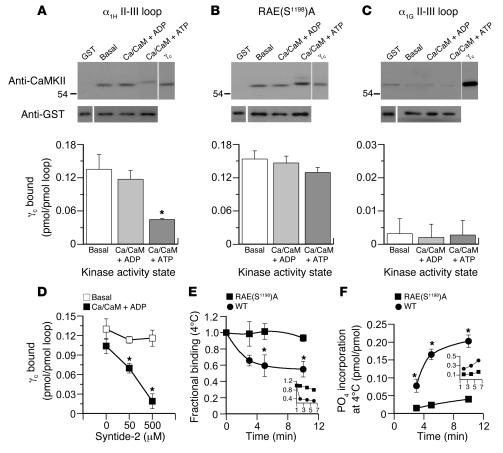
Figure 1. CaMKIIγC binds to the α1H II-III loop and is released by loop phosphorylation.
(A–C) Binding of purified recombinant CaMKIIγC (5 pmol/250 μl) to bead-bound GST-(II-III) loop fusion proteins (2 pmol). Wild-type α1H II-III loop (A), RAE(S1198)A–α1H II-III loop (B), or α1G II-III loop (C) under autoinhibited (basal), activated (Ca2+/CaM + ADP), or autophosphorylated (Ca2+/CaM + ATP) conditions. Upper panels: immunoblots of bound kinase detected by anti-CaMKII antibody; 0.25 pmol standard for comparison. Equal fusion loading was verified independently in parallel runs (see Methods), and anti-GST detection is shown below. Histograms: quantified mean binding data ± SEM for 5 studies. *P < 0.05, Ca2+/CaM + ATP versus basal and Ca2+/CaM + ADP (Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA on Ranks, Dunn’s method). (D) Competition for autoinhibited or Ca2+/CaM + ADP–activated CaMKII/α1H II-III loop by syntide-2. *P < 0.05 (ANOVA, Student-Newman-Keuls method). (E and F) Time course of 4°C CaMKIIγC dissociation and loop phosphorylation following activation of autoinhibited CaMKIIγC prebound to GST–α1H II-III loop fusion proteins [wild type vs. RAE(S1198)A]. Activators, Ca2+/CaM + ATP (0.5 mM/5 μM + 0.5 mM), added at t = 0. (E) Activated-kinase binding determined from quantified immunoblots expressed relative to preactivation values. (F) Phosphorylation stoichiometry of GST–α1H II-III loop fusions determined from 32P incorporation. *P < 0.05, wild type binding at 5 or 10 minutes versus 0 minutes (ANOVA, Student-Newman-Keuls method). Inset: 30°C. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3).