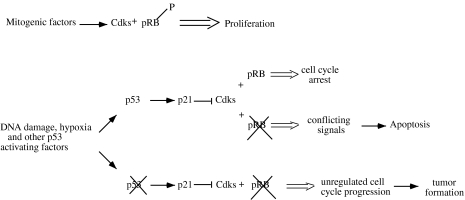
Figure 4.
p53 and pRb cooperation. In normal cells, mitogenic factors and antiproliferative signals regulate cell cycle proliferation and influence the phosphorylation state of pRb. In damaged cells, p53 is activated and causes cell cycle arrest by inducing p21 and by inhibiting pRb phosphorylation by Cdks. If pRb is mutated, the cell cycle is not arrested and the conflict between the p53 signal to stop cell growth and the Cdk signal to proliferate leads to apoptosis. If p53 also is mutated, the cell does not receive a signal to arrest the cell cycle and uncontrolled proliferation leads to tumor formation.