Fig. 2.
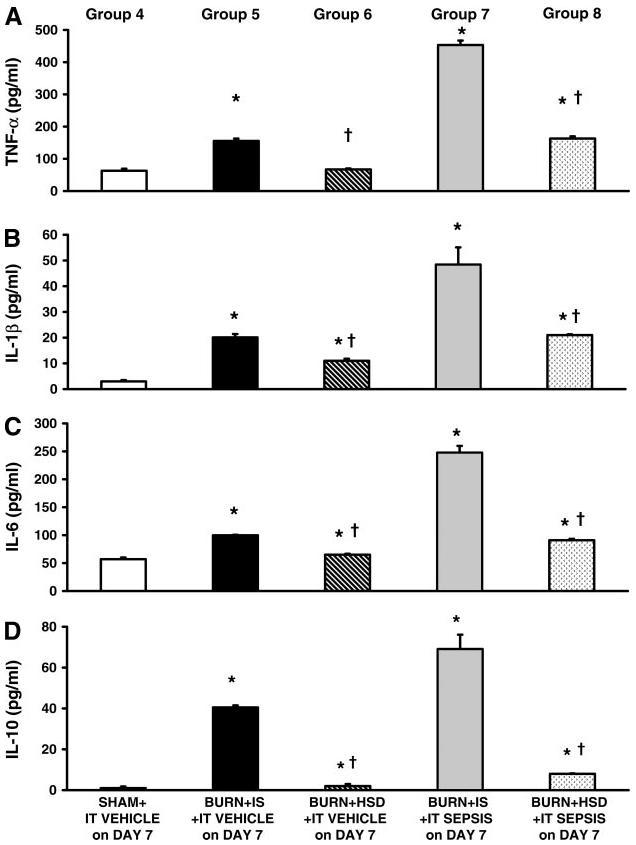
Cardiomyocyte secretion of inflammatory cytokines measured 24 h after either intratracheal (IT) vehicle or septic challenge on postburn day 8. Burns given IS and then septic challenge had significant increases in TNF-α (A), IL-1β (B), IL-6 (C), and IL-10 (D) secretion by cardiomyocytes compared with cytokines secreted by myocytes (pg · 10−4 cells · ml−1) prepared from either burns given IS and IT vehicle on postburn day 7 (group 5) or burn + HSD + IT vehicle on day 7 (group 6). Administration of hypertonic saline during the early postburn period followed by septic challenge on postburn day 7 (group 8) had significant lower TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-10 secretion by cardiomyocytes compared with those measured in burns given IS + an identical septic challenge (group 7). All values are means ± SE. *Significant burn-related differences compared with values measured in sham burn given IT vehicle on postburn day 7 (group 4) (ANOVA and multiple-comparison procedure); †significant differences between HSD and IS (P < 0.05).
