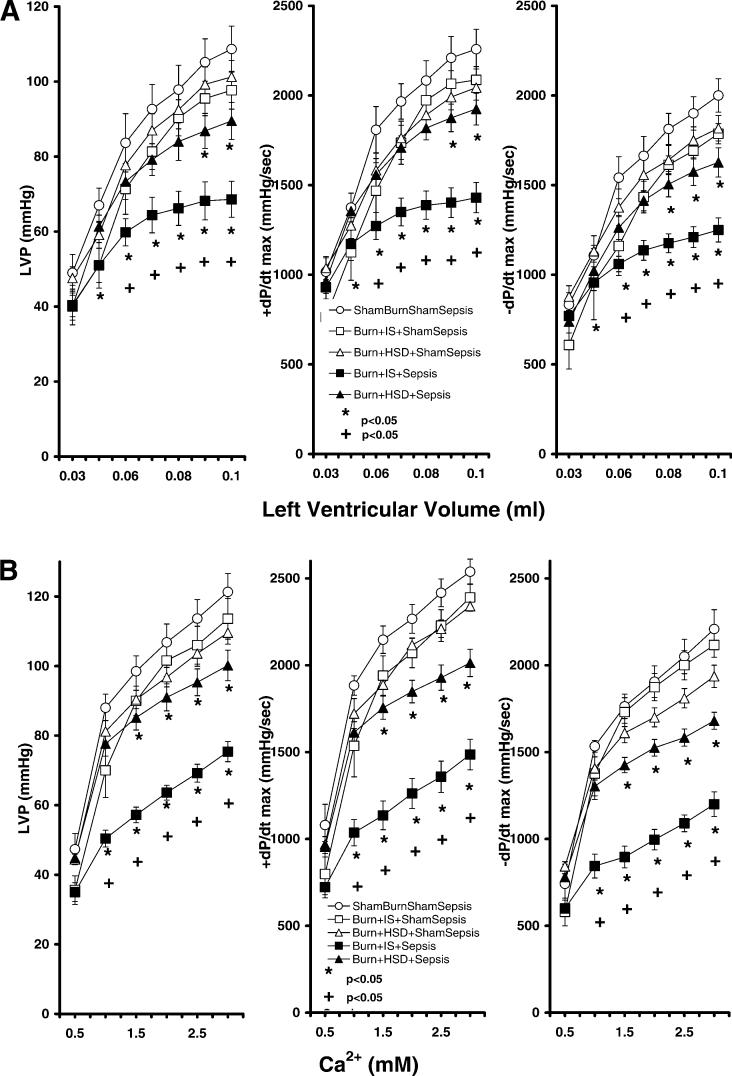
Fig. 4.
Burn injury treated with IS followed by septic challenge on postburn day 7 significantly reduced left ventricular developed pressure (LVP), maximal rate of LVP rise (+dP/dtmax), and maximal rate of LVP fall (−dP/dtmax) responses to either increases in left ventricular volume (A) or increases in perfusate calcium (B) compared with values generated by hearts from sham-burned animals. HSD administration in burned animals attenuated sepsis-related myocardial contractile defects. All values are means ± SE. *Significant differences from sham burn (P < 0.05, ANOVA and Student-Newman-Keuls); +significant differences in burn + HSD + sepsis compared with burn + IS followed by septic challenge (P < 0.05, ANOVA and Student-Newman-Keuls).