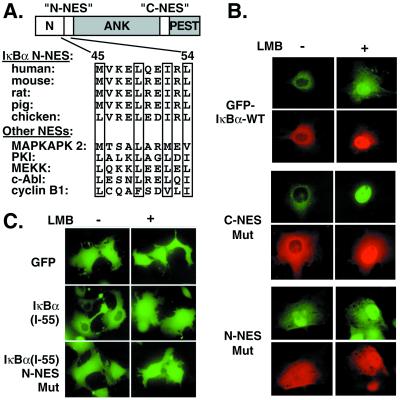
Figure 5.
Identification of N-NES of IκBα. (A) N-NESs in different species are aligned with those of previously characterized shuttling proteins. The critical hydrophobic residues are boxed. ANK, ankyrin repeats; PEST, region rich in proline (P), glutamate (E), serine (S), and threonine (T). (B) GFP-IκBα wild type (WT) (1.0 μg) and GFP-IκBα mutants (1.0 μg) were transfected with p50 and p65 (1.0 μg each) expression vectors into Cos-7 cells and left untreated or treated with LMB (20 ng/ml for 60 min). GFP-IκBα and p65 were covisualized with GFP fluorescence (green) and by staining with p65 antibody (red). In the GFP-IκBα mutants, critical hydrophobic residues (bold) in C-NES (IQQQLGQLTLENLQML) and N-NES (MVKELQEIRLEP) were substituted with Ala. (C) GFP alone, IκBα N-terminal 55, and 55 residues with NES mutations as described above were fused C-terminally to GFP and transfected into Cos-7 cells. GFP and GFP fusion proteins were visualized directly in living cells with GFP fluorescence with or without LMB treatment.