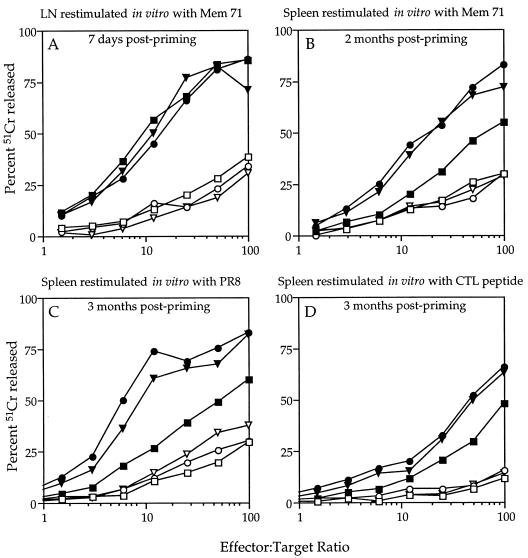
FIG. 5.
Comparison of the lytic activity of cytotoxic T cells from CTL peptide-primed mice versus lipopeptide-primed mice at 7 days and at several months postpriming. A 51Cr release assay was performed by using uninfected P815 targets (open symbols) or Mem 71 virus-infected P815 targets (closed symbols) and various numbers of effector cells. Lymph node effectors (A) or spleen cell effectors (B, C, and D) were generated from mice that had been primed either 7 days (A) or at least 2 months previously (B, C, and D) with 9 nmol of CTL peptide (squares), Pal2-CTL-TH (circles), or Pal4-CTL-TH (triangles) emulsified in CFA. Lymph node or spleen cells were then cultured for 5 days with either virus-infected or peptide-pulsed autologous spleen cells, as indicated above each panel, and then tested in a 51Cr release assay.