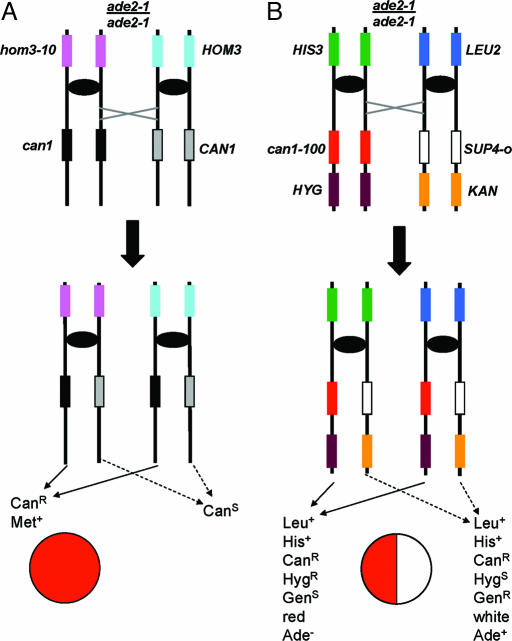
Fig. 1.
Two systems for the detection of mitotic recombination and chromosome loss in diploid yeast cells. (A) One commonly used system for detection of mitotic recombination events uses a diploid that is heterozygous for mutations in the can1 and hom3 loci. The starting diploid strain is CanS and Met+. The depicted strain is also homozygous for the ade2-1 mutation that results in cells that are Ade− and form red colonies. Cells are transferred to plates containing Can, and any CanR derivatives are tested for their ability to grow in the absence of methionine. Met− cells represent chromosome loss events, and Met+ cells are assumed to represent mitotic cross-overs. Note that the CAN1/CAN1 product cannot be selected by this system. (B) Selection of both products of an RCO in the diploid MAB6. The starting diploid is phenotypically CanS GenR HygR His+ Leu+ Ade+/− and forms white colonies. An RCO between the centromere and the CAN1 locus will result in a CanR colony with one red and one white sector, resulting from the growth of two CanR cells, one with the genotype can-100/can1-100 and one with the genotype SUP4-o/SUP4-o. HygS, hygromycin-sensitive; GenS, geneticin-sensitive.