Figure 1.
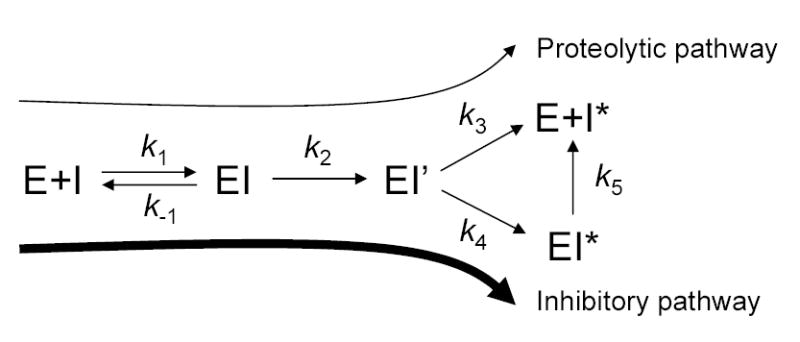
Protease inhibition by the serpin mechanism. I, inhibitor (e.g. α1-antitrypsin); E, enzyme (e.g. trypsin); k1 and k−1 denote the forward and reverse rate constants of the formation of the non-covalent complex EI; k2 is the rate constant of the formation of the acyl-enzyme intermediate EI’; k3 is the rate constant of deacylation, resulting in free enzyme and inactivated, cleaved serpin I*; k4 is the rate constant of the formation of the kinetically trapped, stable covalent complex EI*; k5 is the dissociation rate constant of the covalent complex. Adapted with modifications from [11].
