Figure 6.
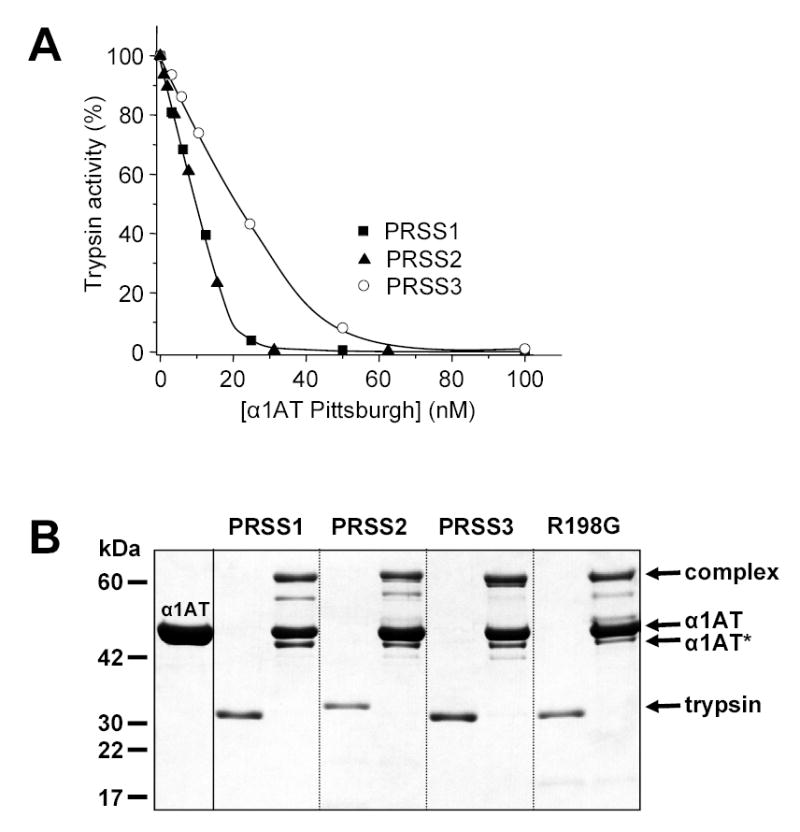
Inhibition of human trypsins by α1-antitrypsin (α1AT) Pittsburgh. A. Cationic trypsin (PRSS1), anionic trypsin (PRSS2) and mesotrypsin (PRSS3) were incubated at 20 nM concentration with the indicated concentrations of α1AT Pittsburgh at room temperature in 100 μL 0.1 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 2 mg/mL BSA, and 1 mM CaCl2 for 10 min. Trypsin activity was then assayed with 0.1 mM N-CBZ-Gly-Pro-Arg-p-nitroanilide (final concentration) and expressed as percentage of initial activity (without inhibition). B. Covalent complex formation between α1-antitrypsin Pittsburgh and human trypsins. Trypsins were incubated at 1 μM concentration with or without 5 μM α1AT Pittsburgh in 0.1 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), and 10 mM CaCl2, at 37 C° for 30 min. The incubation mixtures (100 μL) were precipitated with 10 % final concentration of trichloroacetic acid and subjected to reducing SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. The positions of the bands representing the covalent complex, the free α1AT and the free trypsins are indicated. α1AT* indicates the cleaved, inactive α1AT Pittsburgh. See text for further details.
