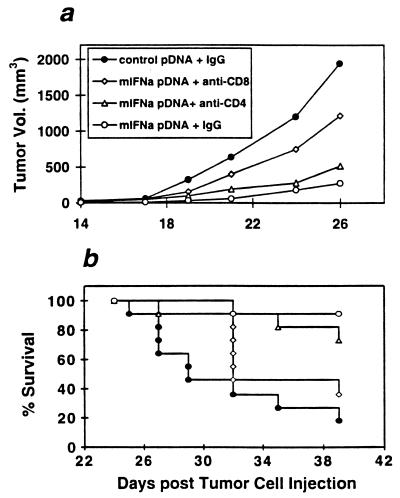
Figure 5.
Evaluation of the role of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in the mIFN-α pDNA antitumor response. Tumor growth (a) and survival (b) are shown for the mice bearing s.c. B16F10 and treated with mIFN-α or control pDNA. Beginning on day 4 after s.c. injection with 104 B16F10 tumor cells, mice were injected i.m. with 100 μg of either the mIFN-α or control pDNA, twice per week for 3 weeks. One day before each pDNA injection, the mice were injected i.p. with 500 μg of either anti-CD4 mAb (clone GK1.5, rat IgG), anti-CD8 mAb (clone 2.43, rat IgG), or normal rat IgG (n = 10 mice per group). Mice injected with the mIFN-α pDNA and treated with normal IgG had a significant reduction in tumor volume (P < 0.003) by day 21 and a significant increase in survival (P < 0.009) compared with the mice injected with control pDNA and treated with normal IgG. Mice injected with mIFN-α pDNA and treated with anti-CD4 mAb still had a significant reduction in tumor volume (P < 0.003) by day 21 and a significant increase in survival (P < 0.009) compared with the controls. In contrast, mice injected with mIFN-α pDNA and depleted of CD8+ T cells had no significant reduction in tumor volume or increase in survival compared with the controls.