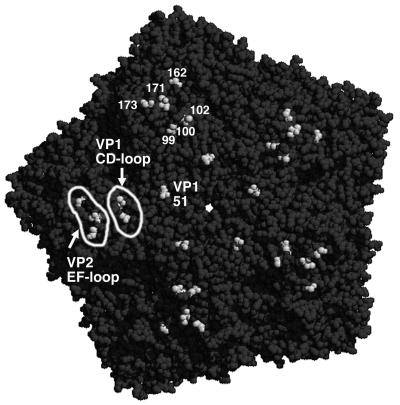
FIG. 10.
Capsid mutations responsible for virus adaptation to CHO-K1 and L929 cells. Shown is a pentamer of the DA1 capsid (seen from outside) in a space-filling view generated with the Rasmol software of Roger Sayle (Biomolecular Structures Group, Glaxo Wellcome) from the structural data of the DA virus (10). The pentamer center is visible as a white hole. Shadows outline the depressions of the capsid surface. Amino acids VP1-99, -100, and -102 (CD loop of VP1), VP2-162, -171, and -173 (EF loop of VP2), and VP1-51 are shown in white. DA capsid amino acids interacting with sialic acid are VP2-161, -163, and -174 and VP3-232 (40), located in the region indicated as the VP2-EF loop. Note that the VP1-51 mutation is shown on the DA pentamer although it occurred in GDVII (at a similar location). These amino acids are all visible from outside, indicating that they are exposed at the capsid surface.