FIGURE 8. Functional effects of mutations of amino acid residues in the IIS4 segment.
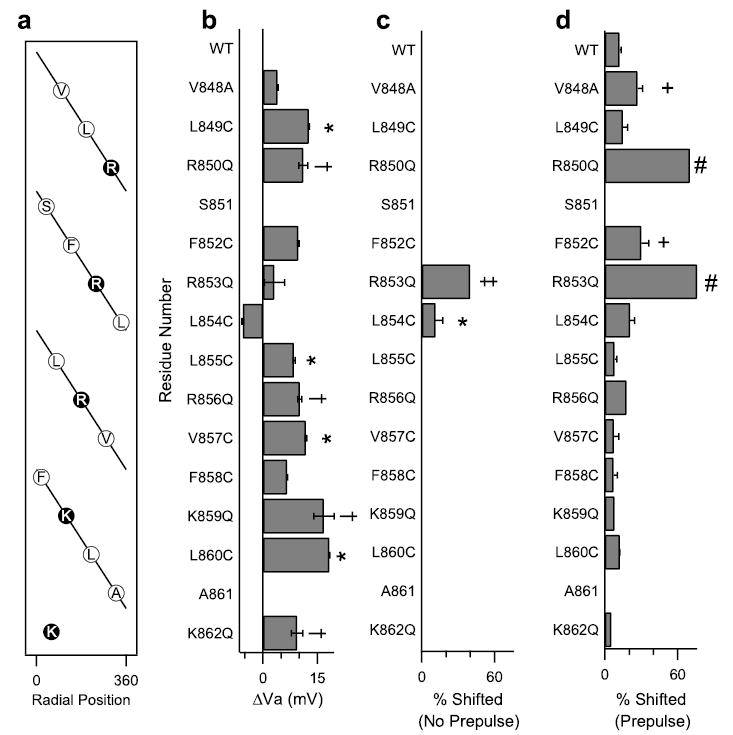
a, a helical net depiction of the amino acids of transmembrane segment IIS4. The charged arginines and lysines are highlighted. b, the shift in the activation curve relative to WT of each IIS4 mutant channels. c, the percentage of channels shifted negatively in the absence of a prepulse in the presence of 200 nm Css IV for each of the mutant channels as indicated by the fit of a two-component Boltzmann equation (see “Experimental Procedures”). *, significant increase relative to WT, p < 0.05. d, the percentage of channels shifted negatively in the presence of a prepulse in the presence of 200 nm Css IV for each of the mutant channels. +, significant increase relative to WT, p < 0.05. Values for R850Q, R853Q, R856Q, K859Q, and K862Q are from Ref. 35. The symbols †, ‡, and # indicate significant effects compared with wild type in panels b– d.
