FIGURE 9. Structural model of β-scorpion toxin binding to Nav1.2.
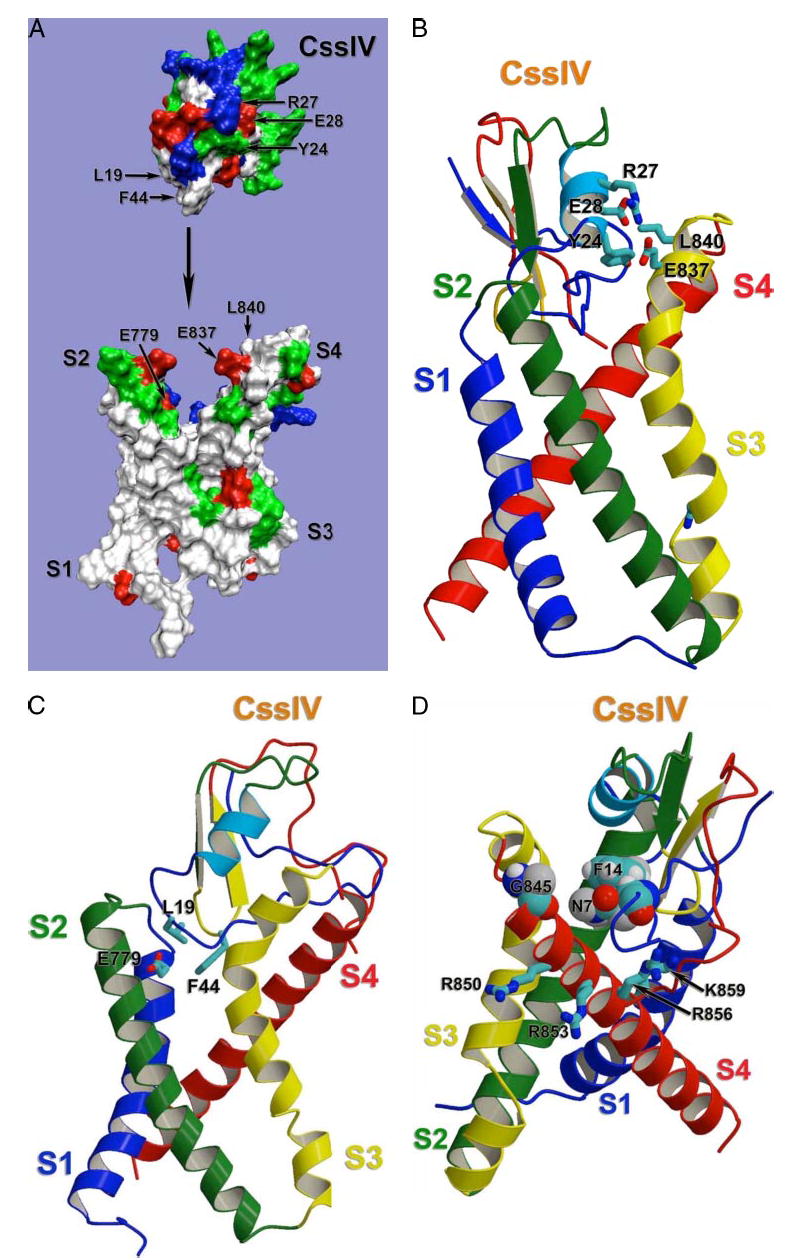
Docking model of β-scorpion Css IV toxin binding to the voltage-sensing segments of domain II of Nav1.2, generated as described under “Experimental Procedures.” A, molecular surface representation of the same view of the model as in panel C. To demonstrate overall shape complementation, β-scorpion Css IV toxin model was separated from the sodium channel model. Side chains of selected residues are labeled with corresponding residue numbers. Side chains are colored as white for hydrophobic residues, blue for positively charged residues, red for negatively charged residues, and green for polar butun charged residues. B, sideview of the ribbon representation of the docking model with the sodium channel transmembrane segments S1 and S4 on the front. Side chains of selected residues are shown in stick representation. C, side view of the ribbon representation of the docking model with the sodium channel transmembrane segments S2 and S3 on the front. Side chains of residues proposed to be important for Na+ channel-Css IV interaction are shown in stick representation. D, side view of the ribbon representation of the docking model with the sodium channel transmembrane segments S3 and S4 on the front. Side chains of residues proposed to be important for Na+ channel-Css IV interaction are shown in stick representation.
