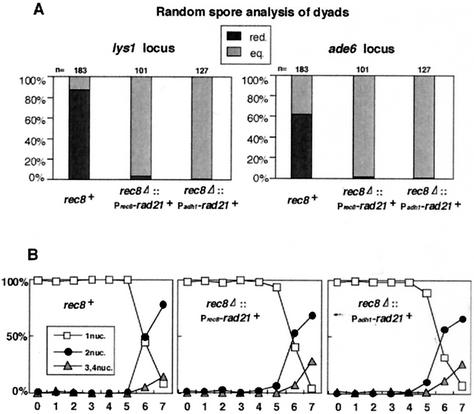
FIG. 5.
rec8Δ cells ectopically expressing rad21+ undergo equational chromosome segregation at meiosis I. (A) Diploid h+/h+ pat1-114 cdc2-L7 rec8+, h+/h+ pat1-114 cdc2-L7 rec8Δ::Prec8-rad21+-GFP, and h+/h+ pat1-114 cdc2-L7 rec8Δ::Padh1-rad21+-GFP cells carrying heterozygous centromere-linked markers (lys1, ade6) (PY221, PY754, and PY770) were induced to synchronous meiosis. Because of the cdc2-L7 mutation, the cells mostly produced dyads. These were treated with glusulase to obtain free spores, which were plated on YE media containing Magdala Red at 26.5°C for 7 days. Diploid colonies were selected as dark red staining and tested for auxotrophy. Cells undergoing reductional division generate dyads with +/+, −/− genotypes ([+], [−] phenotypes) whereas cells undergoing equational division generate dyads with +/−, +/− genotypes ([+], [+] phenotypes). The number of reductional divisions was calculated by n[red.] = n[−] and that of equational divisions was calculated by n[eq.]= (n[+] − n[−])/2. (B) The nuclear divisions during synchronous meiosis in panel A were monitored by DAPI staining. Note that only some cells underwent meiosis II because of the cdc2-L7 mutation.