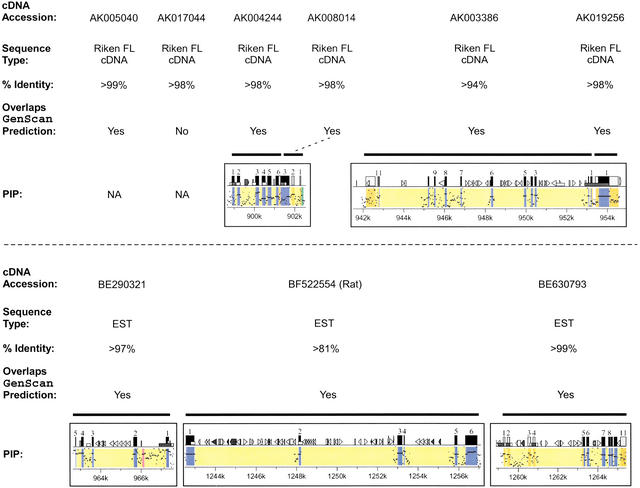
Figure 3.
Identification of previously unreported genes in the Williams syndrome (WS) region. Of the 30 genes identified within the ∼1.4 Mb of finished mouse sequence (see Table 4), 9 have not been previously reported to reside within the WS region. Information about each of these 9 genes is provided (listed in order across the mouse WS region), including (1) a representative GenBank accession number for the mouse cDNA sequence (note in one case, BF522554, the only available cDNA sequence was from rat); (2) the type of sequence contained in that GenBank record (Riken full-length [FL] cDNA sequence [Kawai et al. 2001] or EST); (3) the percent-identity between the mouse genomic sequence and the matching cDNA sequence; (4) an indication of whether or not the putative gene overlaps a GenScan-predicted gene (specifically, if >1 exon matches a Genscan-predicted exon or, in the case of AK019256, the single exon matches the predicted exon for >500 bp; note that the only gene not meeting these criteria, AK017044, did have one of its exons matching a Genscan-predicted exon); and (5) the gene-containing portion of the percent-identity plot (PIP) showing the pattern of mouse–human sequence conservation (except for AK005040 and AK017044, for which no human sequence was available). See Fig. 2 for additional details about the PIP.