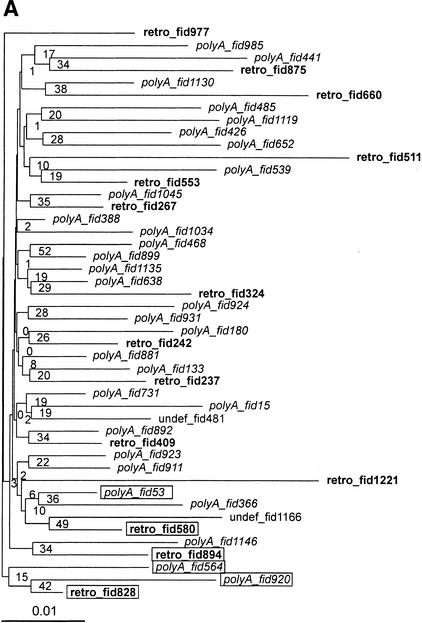
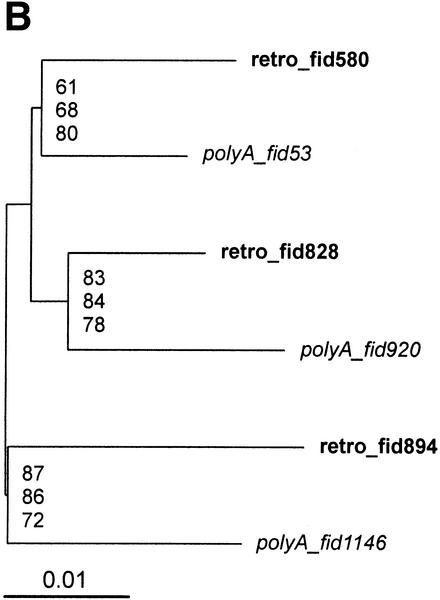
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic trees of HERV-W elements. We selected multiple alignment of the proximal part of the pol region (nucleotides 4450–6789). All gap- and CpG-containing sites were excluded (see Methods). Poly(A) elements are in italics, retroviral copies are in bold to highlight dispersion of poly(A) elements within the retro group. (A) Neighbor-joining tree with 1000 bootstrap replicates. Forty-six elements at 581 non-gap, non-CpG sites. Rectangles show the elements selected for further phylogenetic analysis in Fig. 4B. (B) A subset of 6 elements at 1290 non-CpG, non-gap sites. Topology is based on a maximum likelihood tree, bootstrap values (1000 replicates) ordered from top to bottom show support of the topology for maximum likelihood, maximum parsimony, and neighbor-joining methods implemented in the phylo_win program (see Methods).