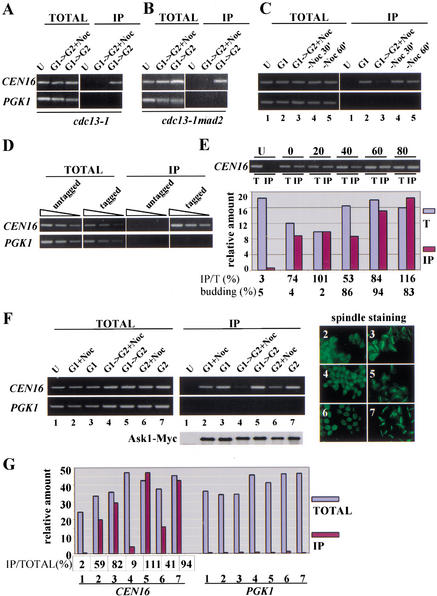
Figure 5.
The association of Ask1 to the centromere requires intact microtubules. (A) Ask1 centromeric binding is inhibited by nocodazole. α-factor-arrested cdc13-1 ASK1–MYC (Y1114) cells were released into prewarmed YPD with (G1–G2 + Noc) or without (G1–G2) nocodazole at 32°C. Seventy minutes later, samples were collected for ChIP analysis. Untagged wild-type cells are included as a control (U). (B) Depolymerization of microtubules, not the activation of the spindle checkpoint, blocks the loading of Ask1 to centromeric DNA. G1-arrested cdc13-1 mad2 (Y1116) cells containing Ask1–Myc were released into medium containing nocodazole for 70 min and processed for ChIP analysis as above. Untagged wild-type cells are included as a control (U). (C) The nocodazole-dependent centromere binding of Ask1 is reversible. α-factor-arrested cdc13-1 ASK1–MYC (Y1114) cells (G1) were released into prewarmed YPD with nocodazole at 32°C (G1–G2 + Noc). Seventy minutes later, cells were spun down and resuspended in fresh YPD at 32°C to remove nocodazole. Samples were collected at 30-min intervals for ChIP analysis (−Noc 30', −Noc 60'). Untagged wild-type cells are included as a control (U). (D) Control showing that the PCR reactions are in the linear range. Twofold serial dilutions of the precipitated and input samples used in lanes 1 and 7 in F were subjected to PCR. (E) The centromere binding of Ask1 in the cell cycle. ASK1–MYC (Y1113) cells were arrested at G1 with α-factor and then released at 30°C. Samples were collected every 20 min for ChIP analysis. DNAs from total (T) and immunoprecipitaed (IP) samples were analyzed and the PCR products were quantitated using NIH image software. Percent budding for the samples is shown below. (F) The centromere binding of Ask1 in G1 and G2-arrested cells is less sensitive to nocodazole treatment. cdc13-1 ASK1–MYC (Y1114) cells were arrested in G1 with α-factor or in G2 by incubating at 32°C before nocodazole was added. Seventy minutes later, samples were collected for ChIP analysis. Cells that were released from G1 to G2 were included as a control (lanes 4,5). (Bottom) The amounts of Ask1–Myc protein immunoprecipitated as determined by Western analysis. (Right) The control showing that nocodazole treatment destabilized microtubules. Shown here are anti-tubulin immunoflourescence images of cells used to prepare the DNA used in lanes 2–7. (G) Quantification of the PCR reactions in F. PCR products in F were run on a 3% agarose gel, visualized with ethidium bromide staining, and scanned for quantitation using NIH Image software.