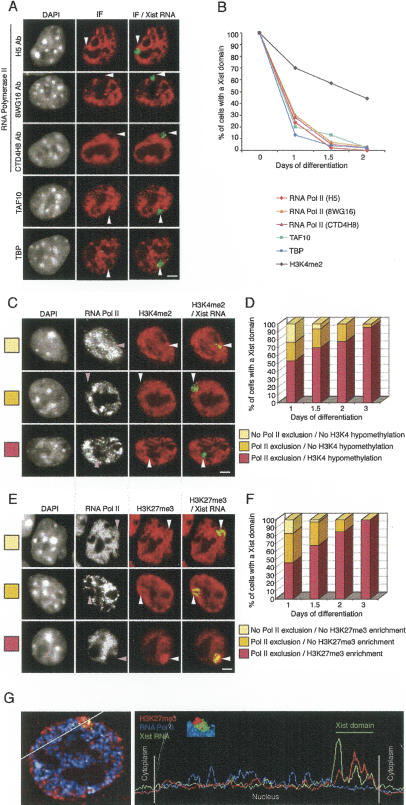
Figure 1.
Exclusion of the transcription machinery from the Xist RNA domain during X inactivation of female ES cells undergoing differentiation. (A) Representative immunofluorescence (IF) using antibodies against several components of the transcription machinery (RNA Pol II, TAF10, and TBP; red) combined with Xist RNA FISH (green) on female ES cells after 2 d of differentiation. Three antibodies (H5, 8WG16, and CTD4H8) recognizing different phosphorylated forms of RNA Pol II were used. Arrowheads indicate the location of the Xist RNA domain. DNA is stained with DAPI (gray). Bar, 5 μm. (B) Kinetics of exclusion of the transcription machinery from the Xist RNA-coated X chromosome during female ES cell differentiation (day 1, n = 60; days 1.5 and 2, n = 100). (C,E) Dual IF for RNA Pol II (H5 Ab; gray) and histone H3K4me2 (C, red) or histone H3K27me3 (E, red) was combined with Xist RNA FISH (green) in female ES cells undergoing differentiation (day 1, top line; day 2, middle line; day 3, bottom line). The Xist RNA domain is shown with an arrowhead. DNA is stained with DAPI (gray). Bar, 5 μm. (D,F) Relative kinetics of the exclusion of the transcription machinery and the appearance of histone modifications during X inactivation on female ES cells undergoing differentiation (day 1, n = 60; days 1.5, 2, and 3, n = 100). (G) Representative example of 3D analysis, 3D reconstruction, and a scan line to demonstrate the relative exclusion of RNA Pol II (blue) and enrichment of H3K27me3 (red) with respect to the Xist RNA domain (green) in female ES cells differentiated for 3 d.