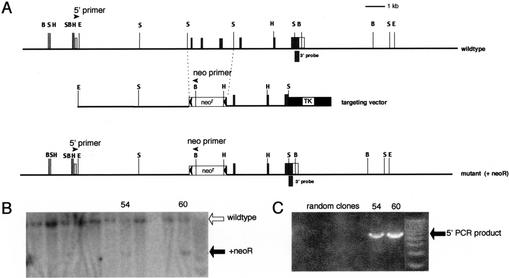
Figure 1.
Targeted disruption of the mouse Gfi-1b gene. (A) Partial restriction map of the mouse Gfi-1b locus (top), the targeting vector (middle), and the expected targeted loci with the floxed neoR cassette (bottom). The 130-bp probe extending from the SacI site to the end of the Gfi-1b coding sequence on exon 7 used to detect appropriate 3′ integration of the targeting vector on Southern blots is indicated (3′ probe). The positions of the primers used to determine the 5′ integration by PCR are also indicated by arrowheads (5′ primer and neo primer, respectively). The Gfi-1b coding exons are indicated as shaded boxes, and the noncoding ones by open boxes. The floxed neoR cassette is indicated by an open box (neoR) flanked by arrowheads (loxP sites), and the TK cassette is shown as a solid black box. The restriction enzyme sites indicated in the map are BamHI (B), EcoRI (E), HindIII (H), and SacI (S). The sizes of the BamHI fragment detected by the 3′ probe in the wild-type and the mutant allele with the inserted neoR cassette are 12 kb and 5 kb, respectively. (B) Southern blot analysis of G148- and gancyclovir-resistant ES cell clones with the 3′ probe. Positions of the wild-type and mutant alleles (with neoR) are indicated by open and solid arrows, respectively. (C) PCR amplification of selected clones shown in B with the 5′ and neo primers, respectively. The PCR product indicative of the homologous recombination is indicated (5′ PCR product).