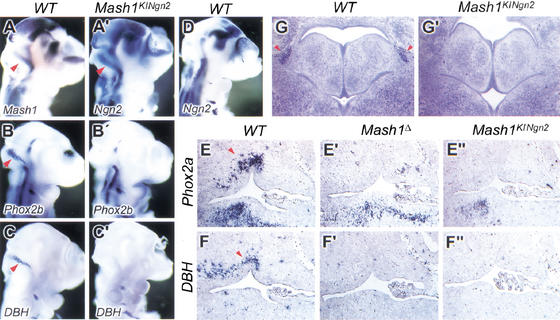
Figure 6.
Ngn2 does not rescue the development of noradrenergic neurons of the locus coeruleus. (A–D, A‘–C‘) Hybridization of E10.5 wild-type (A–D) and Mash1KINgn2embryos (A‘–C‘) embryos with probes for Mash1 (A), Phox2b (B) and DBH (C), showing expression of these genes in precursors of the locus coeruleus, located in the rostral hindbrain near the rhombic lip (arrowheads). Ngn2 is expressed in these precursors in Mash1KINgn2embryos (A‘) and not in wild-type embryos (D). Nevertheless, noradrenergic traits, including expression of Phox2b (B‘) and DBH (C‘) are not induced by Ngn2 in Mash1KINgn2embryos. (E–E", F–F") Sagittal sections at the level of the fourth ventricle in wild-type and mutant embryos at E13.5. Phox2a and DBH are normally expressed by the neurons of the locus coeruleus located anterior and dorsal to the fourth ventricle (arrowheads in E and F, respectively), whereas expression of the two genes is missing at the same location in Mash1Δ (E‘, F‘) and Mash1KINgn2embryos (E", F"). (G, G‘) Nissl stained coronal sections at the level of the pons at birth. The locus coeruleus is recognizable as a compact group of darkly stained neurons lateral to the fourth ventricle (arrowhead in G), which is missing in Mash1KINgn2newborns (G‘).