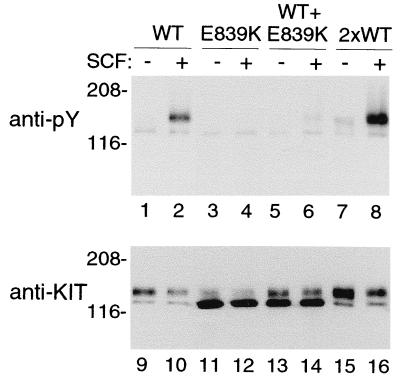
Figure 3.
Dominant–negative effect of Glu839Lys mutant on wild-type KIT phosphorylation. Anti-py blot of immunoprecipitated wild-type and mutant KITs expressed in COS-7 cells. Again, KITWT shows minimal spontaneous phosphorylation but is phosphorylated in response to exogenous SCF (lanes 1 and 2). The E839K mutant is not phosphorylated spontaneously or in response to SCF (lanes 3 and 4). SCF-induced KITWT phosphorylation (lane 2) is decreased dramatically when the wild-type receptor plasmid is transfected with an equal amount of the E839K mutant plasmid (lanes 5 and 6). As a control, a double amount of KITWT plasmid (2×) was transfected (lanes 7 and 8). Spontaneous and SCF-induced phosphorylation were both increased compared with the lower amounts of KITWT plasmid (compare lanes 1 and 2 with 7 and 8). Reprobing of the anti-Py blot (after stripping) with anti-KIT Ab shows the amount of protein in each lane. Long exposure documents a minor component of 145-kDa KITE839K (lanes 11 and 12). The amounts of 125- and 145-kDa KIT in lanes 13 and 14 equals approximately the sum of these two forms expressed separately (lanes 9 and 10, KITWT; lanes 11 and 12, KITE839K). The increase in protein in the control 2× transfected KITWT (lanes 15 and 16) over the 1× KITWT transfectant is comparable to the increase in phosphorylation (lanes 15 and 16 vs. lanes 9 and 10). Molecular markers are indicated in kilodaltons on the left.