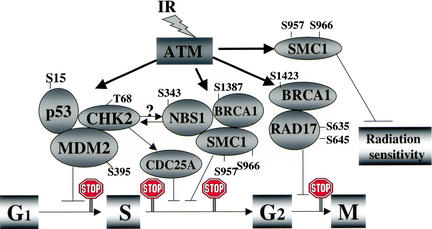
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of direct targets of ATM that affect cell cycle perturbations and modulation of sensitivity to ionizing irradiation. Following ionizing irradiation, the Atm protein kinase is activated and then phosphorylates target proteins. The exact serines (S) or threonine (T) known to be phosphorylated by Atm are listed by number for the various proteins. Chk2, p53, and Mdm2 participate in the G1 arrest, phosphorylation of Nbs1, Brca1, Smc1, and Chk2 have been implicated in controlling the S phase arrest, and phosphorylation of Brca1 and Rad17 are reported to be involved in the G2 arrest. Although phosphorylation of Chk2 has been reported to be dependent on Nbs1 (Buscemi et al. 2001), the exact relationship of the Chk2/Cdc25A axis to Nbs1/Brca1/Smc1 in controlling the S phase checkpoint remains to be clarified. On the basis of the data shown here, phosphorylation of serines 957 and 966 in Smc1 are included as targets involved in the ionizing irradiation-induced S phase arrest and are also implicated in modulating radiation sensitivity.