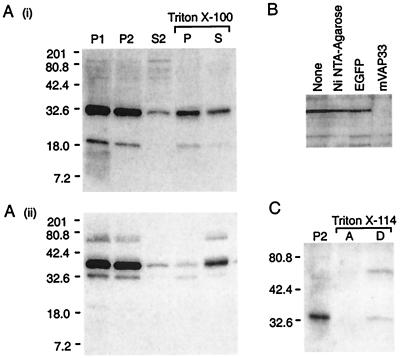
Figure 3.
(A) Western blot analysis of fractionated mouse brain homogenate with mVAP33-specific polyclonal antiserum. (i) The major immunoreactive signal of ≈33 kDa is enriched in the pelleted fractions, but it is only partially extracted into the soluble fraction by 1% (vol/vol) Triton X-100. The cofractionating 19-kDa signal may be the result of proteolysis. (ii) In contrast, the t-SNARE syntaxin, although present in P1 and P2, is almost completely extracted by Triton X-100. The lower-molecular-weight signal is the result of incomplete stripping of the mVAP33 antisera. Molecular markers are Kaleidoscope Prestained Standards (Bio-Rad). (B) The 33-kDa immunoreactivity is specific for mVAP33. The antisera were preincubated with Ni-NTA-agarose with or without recombinant protein. Ni-NTA-agarose, or Ni-NTA-agarose and His6-tagged recombinant green fluorescent protein (EGFP) have no affect, whereas His6-tagged recombinant mVAP33 specifically depletes the 33-kDa signal. (C) mVAP33 is an integral membrane protein. P2 was extracted with 1.5% Triton X-114 and separated into aqueous (A) and detergent (D) phases at 37°C. The 33-kDa immunoreactivity partitions into the detergent phase, indicating that, like the molluscan protein, mVAP33 is an integral membrane protein. After Triton X-114 extraction, mVAP33 appears to form an SDS-stable oligomer of approximately 66 kDa.