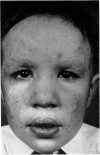
Abstract
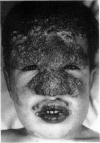
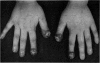
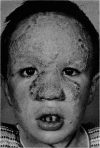
A boy aged 6 years with severe chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis of the granulomatous variety has been treated with the dialysable transfer factor. Before the treatment he was unable to express delayed hypersensitivity. His lymphocytes were able, however, to produce migration inhibitory factor following in vitro challenge with soluble candida antigens, but this activation was not accompanied by a significant increase in DNA synthesis.
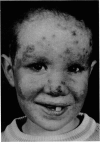
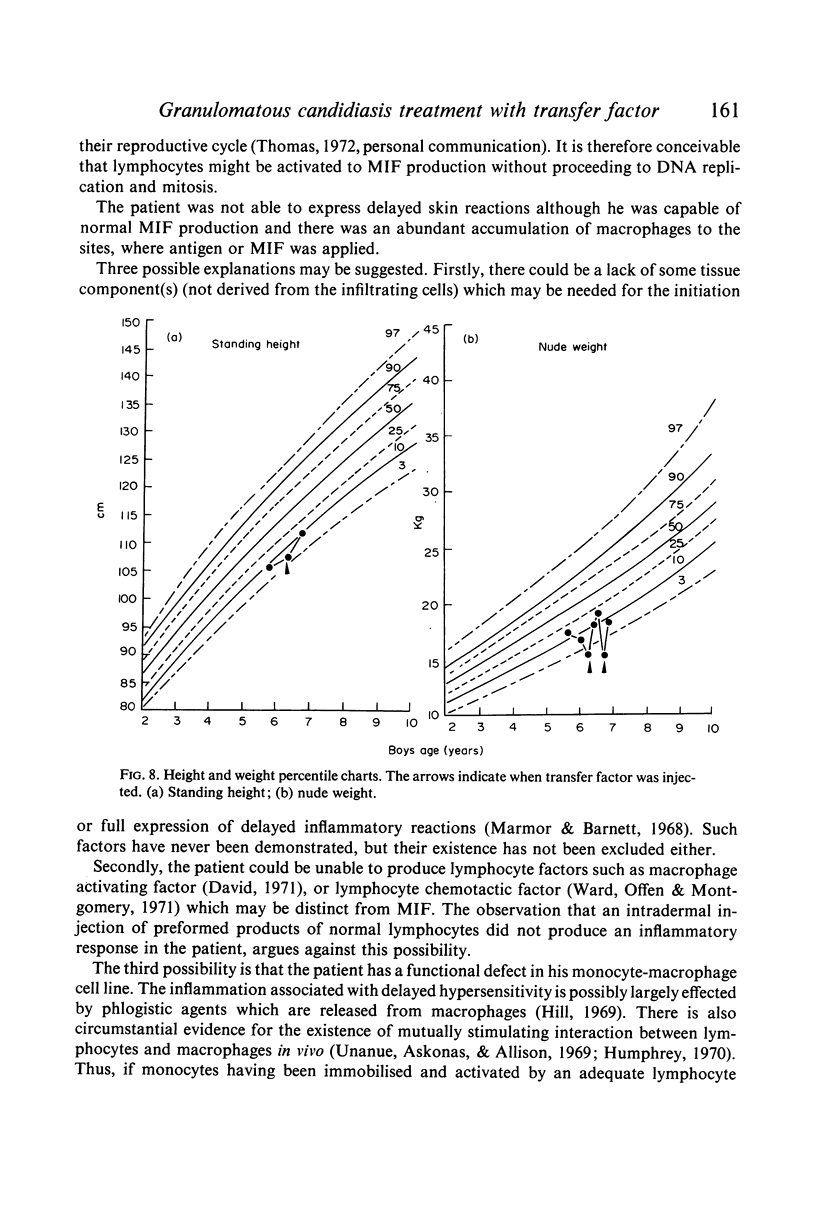
The treatment resulted in a temporary clinical improvement and return to normal of his immune responses. After a relapse he was, 6 months later, once more injected with transfer factor, which again proved effective.
Evidence is presented which suggests a defect of monocyte-macrophage function in this patient and the pathogenesis of candida granulomata is discussed. It is postulated that an amplifying mechanism involving lymphocyte-macrophage interaction is required for the normal expression of delayed hypersensitivity reactions and the effective elimination of Candida albicans.
Full text
PDF
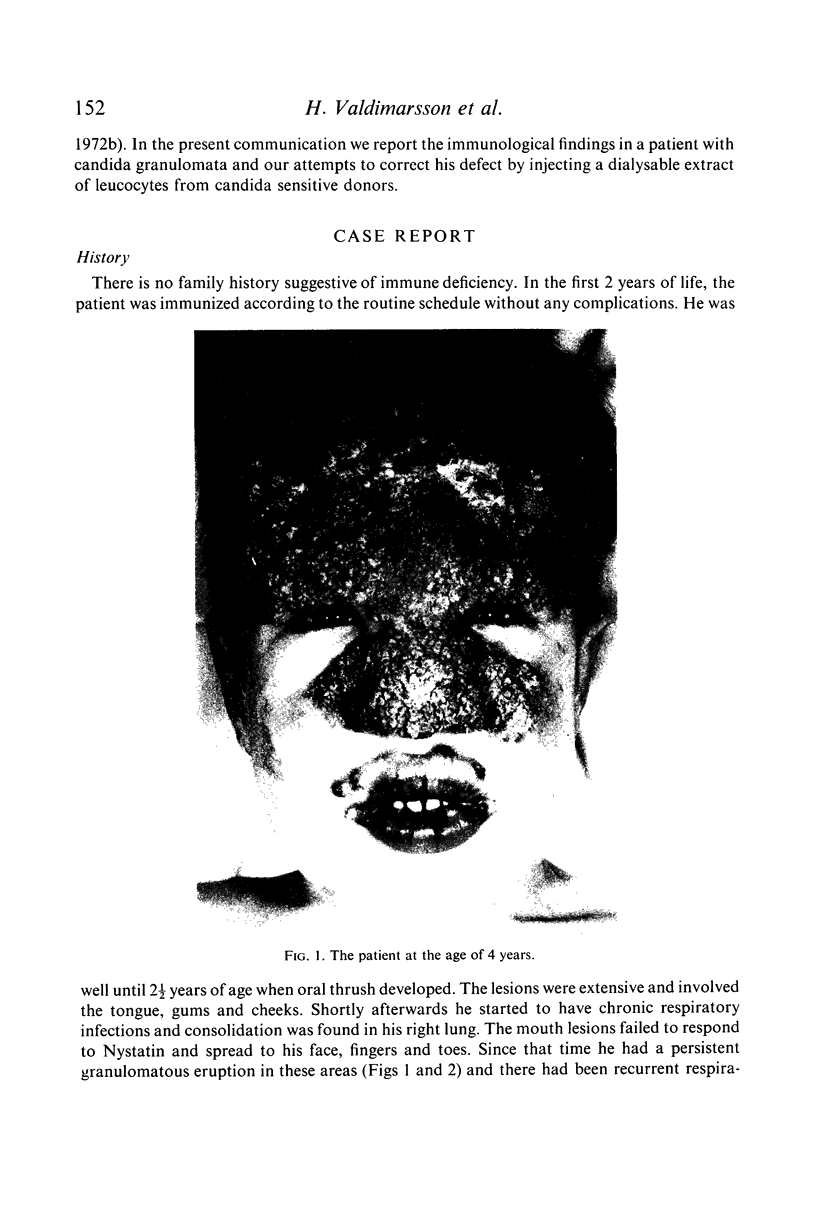
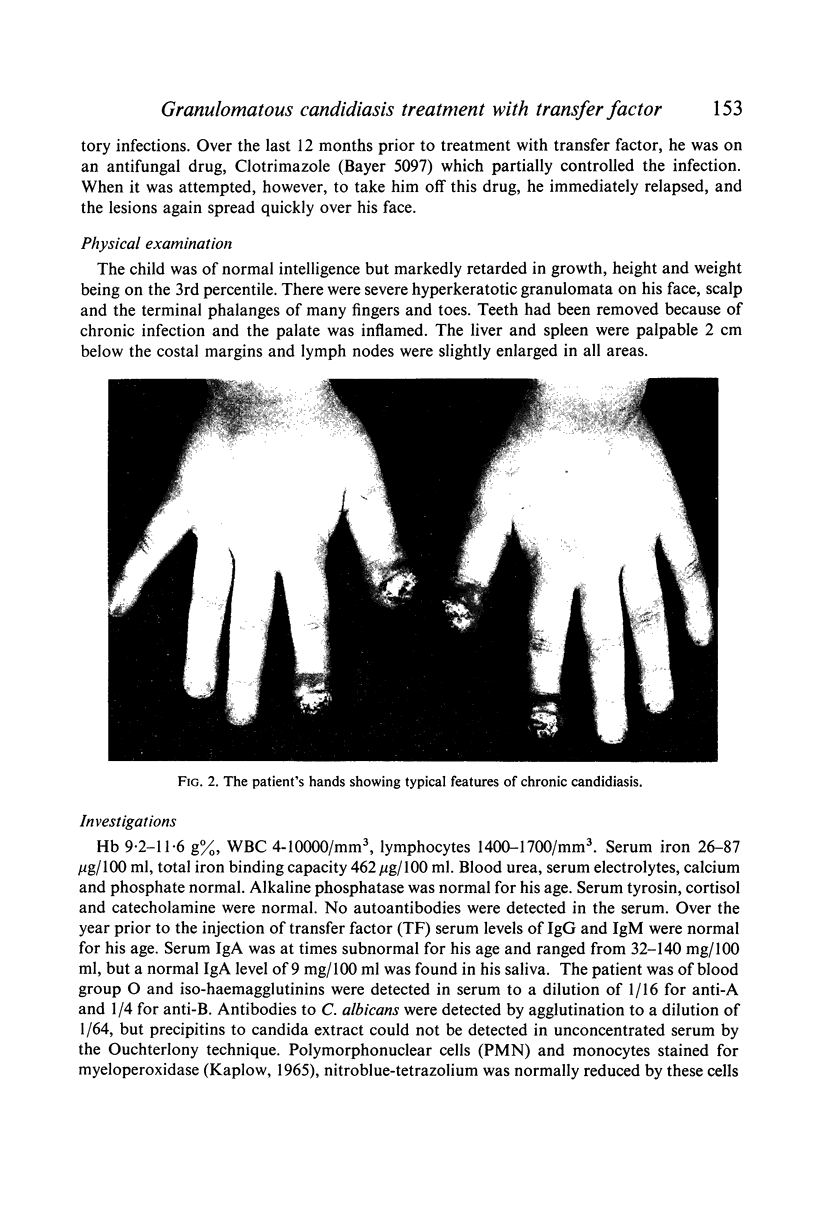


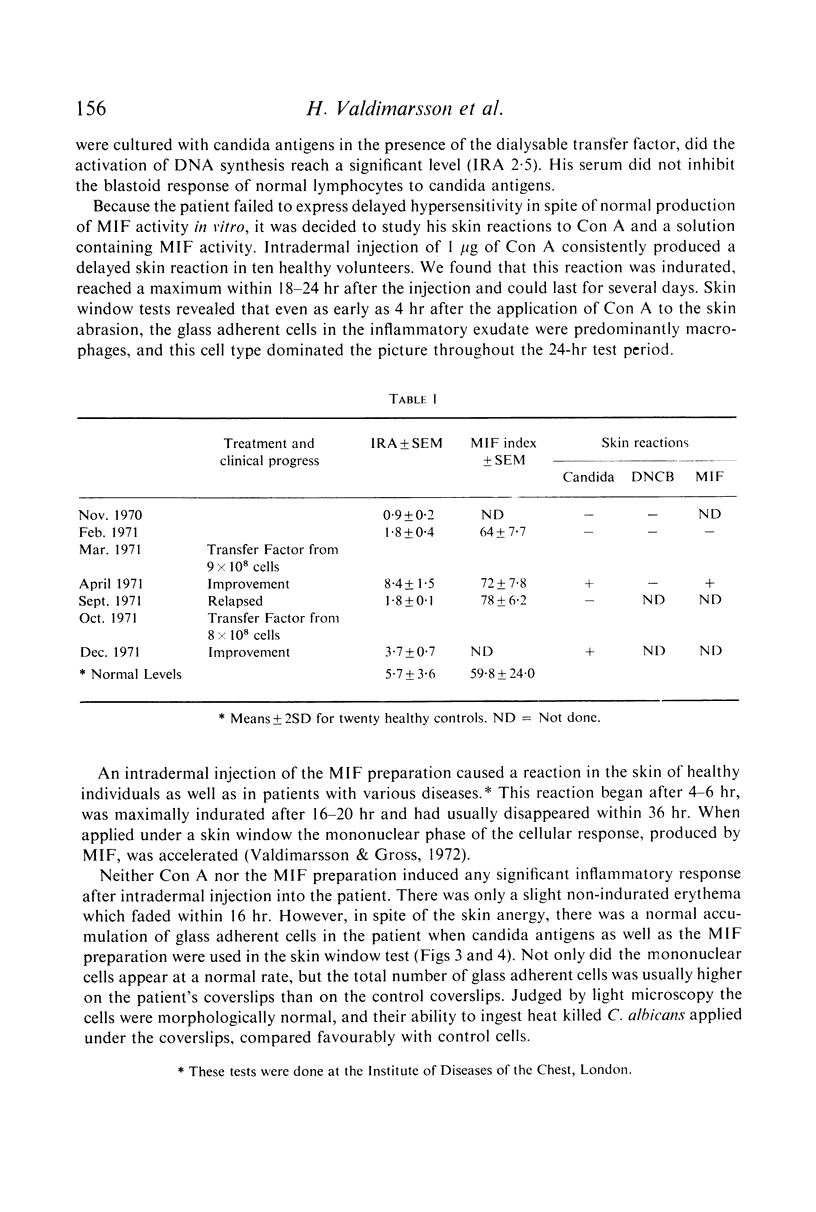


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehner R. L., Nathan D. G. Quantitative nitroblue tetrazolium test in chronic granulomatous disease. N Engl J Med. 1968 May 2;278(18):971–976. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196805022781801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. R. Mediators produced by sensitized lymphocytes. Fed Proc. 1971 Nov-Dec;30(6):1730–1735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. C. The influence of the cellular infiltrate on the evolution and intensity of delayed hypersensitivity reactions. J Exp Med. 1969 Feb 1;129(2):363–370. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLOW L. S. SIMPLIFIED MYELOPEROXIDASE STAIN USING BENZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE. Blood. 1965 Aug;26:215–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick C. H., Rich R. R., Bennett J. E. Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis: model-building in cellular immunity. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Jun;74(6):955–978. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-74-6-955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey R. W., Bruten D. M., Gillespie W. A., Lewis E. L. Trimethoprim-resistant coliforms. Lancet. 1972 Feb 19;1(7747):409–410. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90857-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Cline M. J. Interaction of Candida albicans with human leukocytes and serum. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):996–1004. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.996-1004.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmor M. F., Barnett E. V. Cutaneous anergy without systemic disease. A syndrome associated with mucocutaneous fungal infection. Am J Med. 1968 Jun;44(6):979–989. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REBUCK J. W., CROWLEY J. H. A method of studying leukocytic functions in vivo. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1955 Mar 24;59(5):757–805. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1955.tb45983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitler L., Huber H., Fudenberg H. H. Inhibition of capillary migration by antigen-antibody complexes. J Immunol. 1969 Feb;102(2):404–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Askonas B. A., Allison A. C. A role of macrophages in the stimulation of immune responses by adjuvants. J Immunol. 1969 Jul;103(1):71–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdimarsson H., Holt L., Riches H. R., Hobbs J. R. Lymphocyte abnormality in chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. Lancet. 1970 Jun 13;1(7659):1259–1261. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91742-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Offen C. D., Montgomery J. R. Chemoattractants of leukocytes, with special reference to lymphocytes. Fed Proc. 1971 Nov-Dec;30(6):1721–1724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]