Abstract
Incubation of sensitized peritoneal or pleural cells, or isolated mast cells, taken from rats previously infected with the nematode, Nippostrongylus brasiliensis, but not of cells taken from parasite-free controls, with concanavalin A in vitro induces the release of histamine. The release mechanism triggered by Con A is virtually completed within 60 sec, depends on temperature, but not on the presence of complement, and is inhibited by sympathomimetic amines. It therefore shows striking similarities to the anaphylactic reaction induced by the specific allergen.
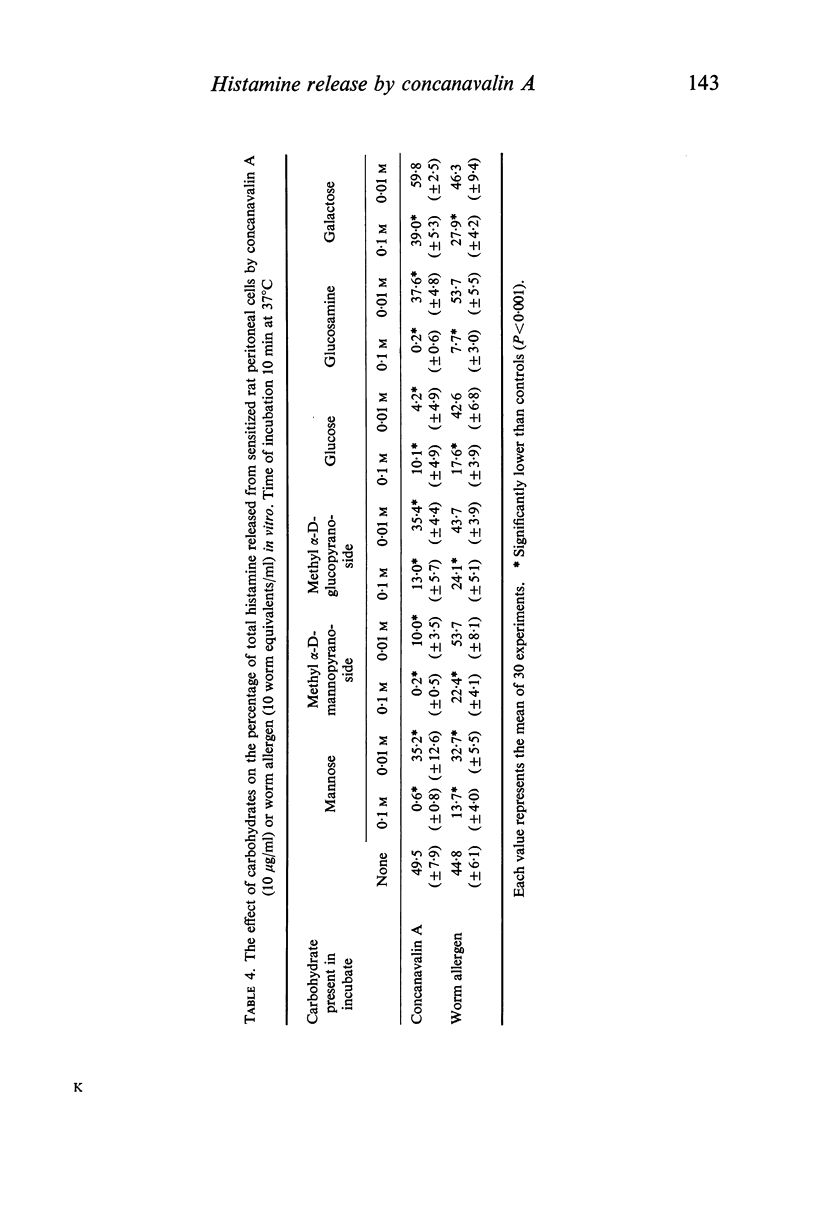
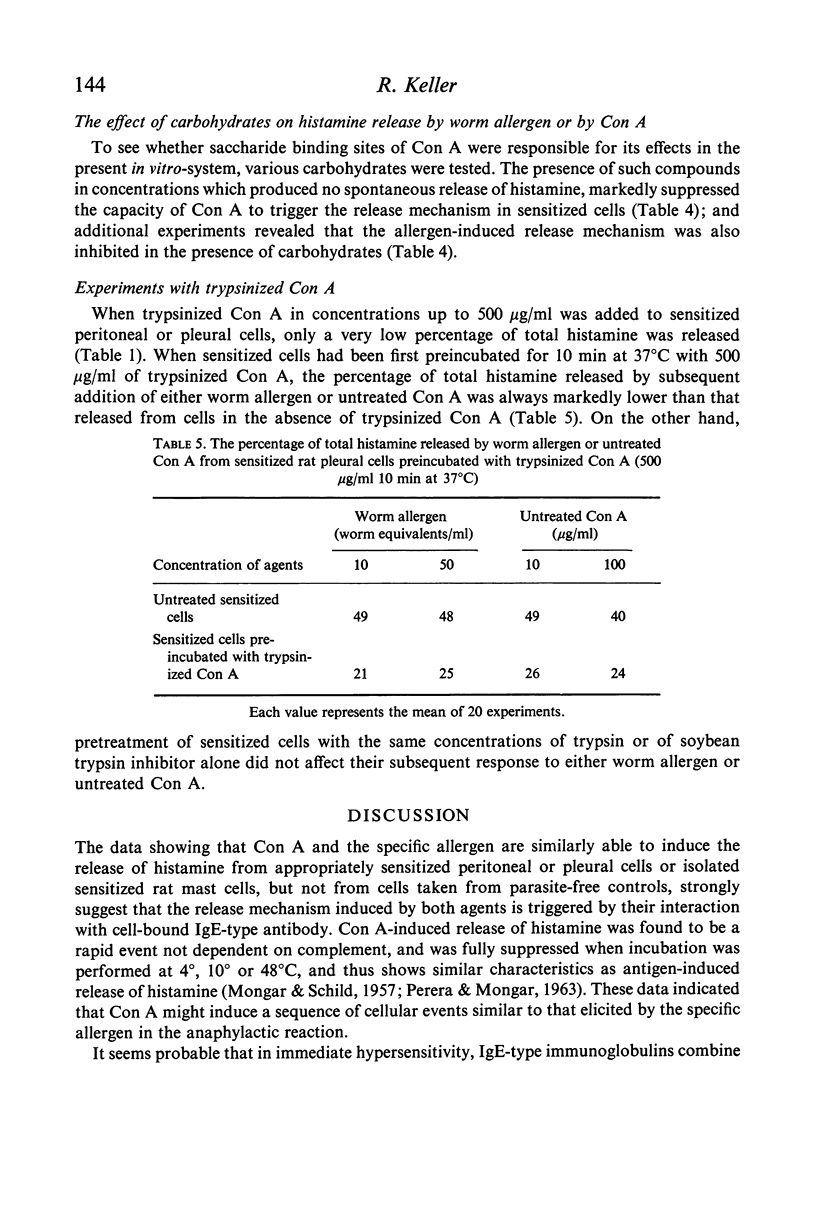
The mechanism by which histamine release is triggered by Con A is discussed, considering the observations that trypsinized Con A is no longer able to induce histamine release, that the presence of high concentrations of trypsinized Con A inhibits the release of histamine by subsequently added Con A or allergen, and that certain carbohydrates inhibit the release of histamine induced by both Con A and allergen. Although some of the data suggest a similarity in the structure of the antigenic determinant in the Fab fragment of IgE and the receptor site for Con A, it seems more likely that Con A is reacting mainly by cross-linking of Fc regions of the immunoglobulin molecule.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assem E. S., Schild H. O. Inhibition by sympathomimetic amines of histamine release by antigen in passively sensitized human lung. Nature. 1969 Dec 6;224(5223):1028–1029. doi: 10.1038/2241028a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger M. M., Noonan K. D. Restoration of normal growth by covering of agglutinin sites on tumour cell surface. Nature. 1970 Nov 7;228(5271):512–515. doi: 10.1038/228512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN I. J., HOLLERMAN C. E., MERRICK J. M. PROTEIN-CARBOHYDRATE INTERACTION. I. THE INTERACTION OF POLYSACCHARIDES WITH CONCANAVALIN A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 4;97:68–76. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90270-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. J., So L. L., Yang Y., Callies Q. C. Protein-carbohydrate interaction. XIX. The interaction of concanavalin A with IgM and the glycoprotein phytohemagglutinins of the waxbean and the soybean. J Immunol. 1969 Oct;103(4):695–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T. Biological function of gamma E antibodies and mechanisms of reaginic hypersensitivity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Jan;6(1):25–42. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T. Reversed type allergic skin reactions by anti-gamma-E-globulin antibodies in humans and monkeys. J Immunol. 1968 Mar;100(3):554–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K., Orange R. P., Austen K. F. Pharmacologic inhibition of the antigen-induced release of histamine and slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A) from monkey lung tissues mediated by human IgE. J Immunol. 1971 May;106(5):1267–1273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones V. E., Ogilvie B. M. Reaginic antibodies and immunity to Nippostrongylus brasiliensis in the rat. II. Some properties of the antibodies and antigens. Immunology. 1967 May;12(5):583–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLER R., BEEGER I. Anaphylaxis in isolated rat mast cells. I. Effect of peptidase substrates and inhibitors. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1963;22:31–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R. Immune reactions to Nippostrongylus brasiliensis in the rat. I. Characteristics of primary and secondary immune response in vivo. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;37(2):197–215. doi: 10.1159/000230233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R. Immune reactions to Nippostrongylus brasiliensis in the rat. II. Primary and secondary immune response: in vitro characterization. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;38(3):305–314. doi: 10.1159/000230283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R., Mueller-Eckhardt C., Kayser F. H., Keller H. U. Interrelations between different typs of cells. I. A comparative study of the biological properties of a cationic polypeptide from lysosomes of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and other cationic compounds. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;33(3):239–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leon M. A. Concanavalin A reaction with human normal immunoglobulin G and myeloma immunoglobulin G. Science. 1967 Dec 8;158(3806):1325–1326. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3806.1325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein L. M., Margolis S. Histamine release in vitro: inhibition by catecholamines and methylxanthines. Science. 1968 Aug 30;161(3844):902–903. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3844.902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONGAR J. L., SCHILD H. O. Effect of temperature on the anaphylactic reaction. J Physiol. 1957 Feb 15;135(2):320–338. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOTA I. THE BEHAVIOR OF MAST CELLS IN ANAPHYLAXIS. Int Rev Cytol. 1963;15:363–397. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61121-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGILVIE B. M. REAGIN-LIKE ANTIBODIES IN ANIMALS IMMUNE TO HELMINTH PARASITES. Nature. 1964 Oct 3;204:91–92. doi: 10.1038/204091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERERA B. A., MONGAR J. L. THE ROLE IN ANAPHYLAXIS OF A CHYMOTRYPSIN-LIKE ENZYME IN RAT MAST CELLS. Immunology. 1963 Sep;6:478–483. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poretz R. D., Goldstein I. J. An examination of the topography of the saccharide binding sites of concanavalin A and of the forces involved in complexation. Biochemistry. 1970 Jul 7;9(14):2890–2896. doi: 10.1021/bi00816a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanworth D. R. Immunochemical mechanisms of immediate-type hypersensitivity reactions. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Jan;6(1):1–12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanworth D. R. Immunoglobulin E (reagin) and allergy. Nature. 1971 Oct 1;233(5318):310–316. doi: 10.1038/233310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner J. B., Howell S. F. Identification of Hemagglutinin of Jack Bean with Concanavalin A. J Bacteriol. 1936 Aug;32(2):227–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.32.2.227-237.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


