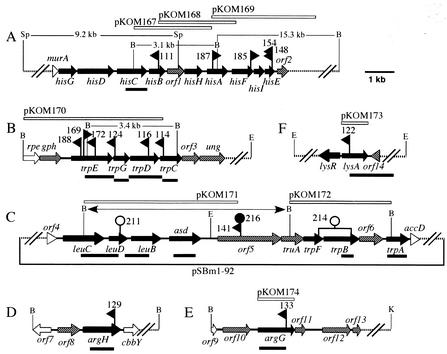
FIG. 4.
Organization of the ATCC 17616 gene clusters covering the TnMod-RTp′ insertion sites. The dashed lines indicate the regions not sequenced. Arrows indicate the deduced transcriptional directions of the genes: black arrows represent the genes directly involved in amino acid biosynthesis, shaded arrows represent the genes postulated not to be directly involved in amino acid biosynthesis, and open arrows and open triangles represent the 5′- or 3′-truncated genes not directly involved in amino acid biosynthesis. The flags represent the positions of the TnMod-RTp′ insertion sites, and the mutant names (without the prefix BT) are indicated. The rightward and leftward directions of the flags represent the orientations of the TnMod-RTp′ inserts such that the transposon-specified Tpr genes are located at the right and left ends (Fig. 2), respectively. The open and filled circles above the map in panel C indicate the positions of the pUC4K- and Ω-Km-derived Kmr genes, respectively, that were inserted into the ATCC 17616 genome to disrupt the wild-type allele, and the names of the resulting mutants (without the prefix BT) are indicated. The open bars above the maps indicate the wild-type genomic regions on the pKOM series of plasmids, whereas the filled bars below the maps indicate the DNA fragments used as the probes for Southern hybridization analysis. The BamHI fragment in pBTB141 is indicated by the double-headed arrow above the map in panel C. Abbreviations for restriction sites: B, BamHI; E, EcoRI; K, KpnI; and Sp, SphI.